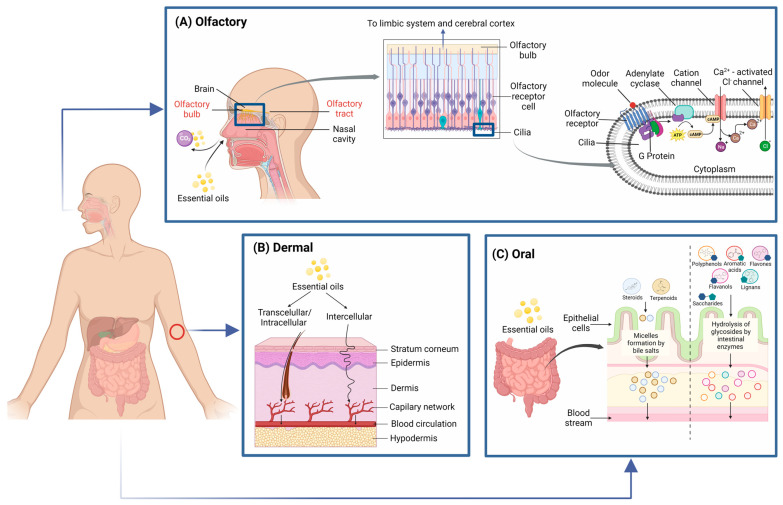
Figure 1.
Essential oils (EO) absorption mechanisms. (A) Olfactory administration. Odor compounds bind to cilia in olfactory receptor cells, which activates G protein-coupled receptors to depolarize cell membranes and promote signal transduction to the limbic system and cerebral cortex. (B) Dermal administration. EO can penetrate the stratum corneum and reach the bloodstream through transcellular or intercellular permeation. (C) Oral administration. Due to their lipophilic character, terpenoids and steroids can be easily absorbed in the small intestine through lipid metabolism. Saccharide-conjugated molecules must be hydrolyzed and then metabolized in the small intestine.