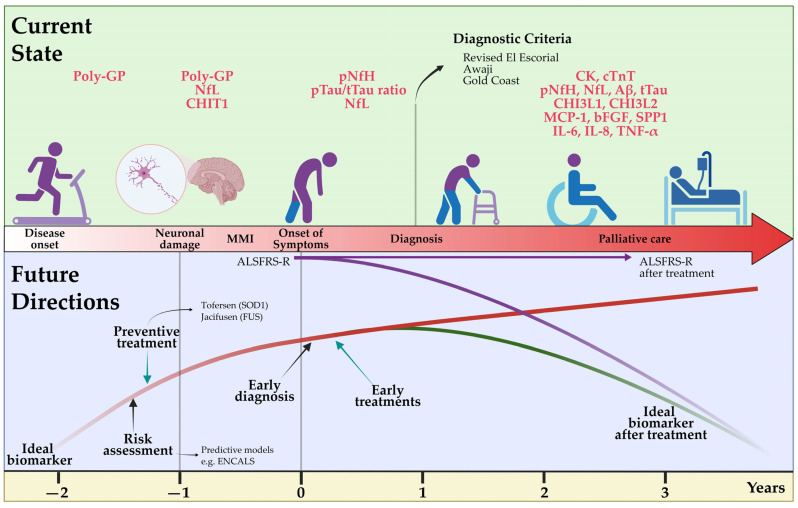
Figure 2.
Current state of and future directions for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A delayed diagnosis of ALS is still currently performed using clinical criteria such as Revised El Escorial, but the determination of fluid biomarkers such as Nf is accelerating an earlier identification of the disease. In the future, the availability of more specific biomarkers related to disease pathology onset will allow early risk assessment and definitive diagnosis in patients in prodromal phases. Additionally, an ideal biomarker should develop preventive therapies and monitor disease activity in patients under novel causative therapies. ALSFRS-R: Revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale; Aβ: Amyloid β; bFGF: basic fibroblast growth factor; CHI3L1: chitinase-3-like protein 1; CHI3L2: chitinase-3-like protein 2; CHIT1: chitotriosidase 1; CK: creatinine kinase; cTnT: cardiac troponin T; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-8: interleukin-18; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MMI: mild motor impairment; NfL: neurofilament light chain; pNfH: phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain; Poly-GP: arginine containing dipeptide repeat polymers; pTau: phosphorylated tau; SPP1: secreted phosphoprotein 1; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor; t-Tau: total tau. Created by Castro-Gomez with “BioRender.com”; accessed on 04 February 2023.