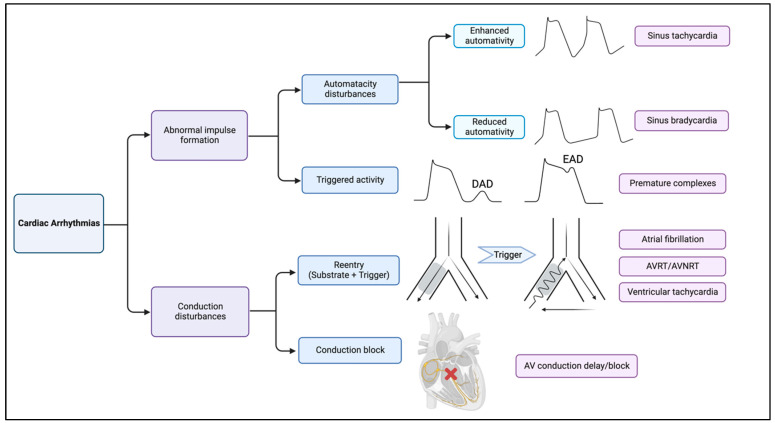
Figure 1.
Summary of molecular mechanisms of arrhythmias. Cardiac arrhythmias can be divided to abnormal impulse formation (also termed as focal activity) and conduction disturbances. Automaticity problems involve both enhanced and reduced automaticity, which are the etiology of sinus tachycardia and bradycardia, respectively. Early and late after depolarization is the common mechanism of both atrial and ventricular premature complexes. Reentrant tachyarrhythmias as a conduction disturbance usually involve both substrate (reduced conduction velocity) and trigger where an impulse circles back to re-excite the myocardium through retrograde conduction via the area of functional block. Conduction delay/block also belongs to conduction disturbances.