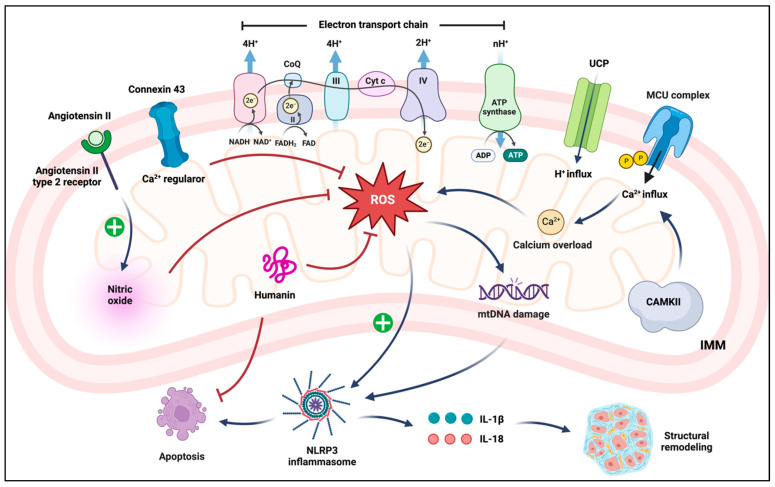
Figure 3.
Overview of mitochondrial proteins in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology. A variety of proteins are involved in the functional maintenance of mitochondria. CAMKII activates MCU and allows mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, which contributes to ROS production. ROS, along with related mitochondrial DNA damage, contribute to the activation of inflammasomes and subsequent cell death. Structural remodeling induced by inflammatory cytokines produced by inflammasomes follows. On the other hand, the increased level of nitric oxide via activation of angiotensin II type 2 receptor, elevation of mitochondrial connexin located on the inner mitochondrial membrane, and augmentation of humanin peptides all contribute to the mitigation of ROS.