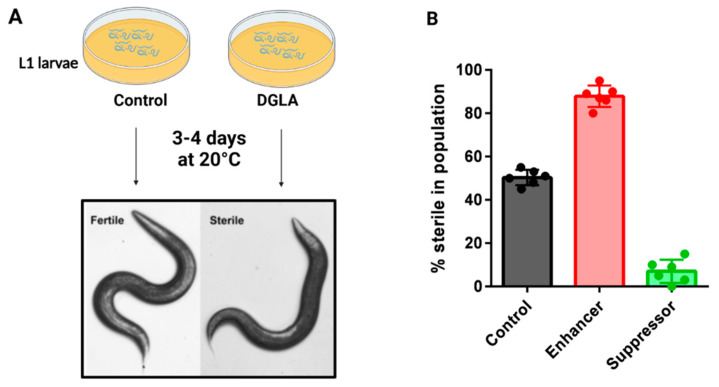
Figure 3.
Dietary DGLA causes ferroptosis of germ cells and sterility in C. elegans. (A) Schematic of the C. elegans fatty acid supplementation assay. Synchronized L1 larvae are plated onto agar plates containing DGLA and dietary E. coli, and incubated at 20 degrees until they reach adulthood, when they are scored as fertile or sterile. Sterile worms lack gametes due to ferroptosis of germ cells during development. (B) Mutant strains that are more sensitive to DGLA are known as enhancers, while mutant strains that are less sensitive to DGLA are known as suppressors. Often, enhancer strains contain mutations in protective genes, such as genes encoding GPX enzymes or genes required for MUFA production. Suppressor genes include genes needed to produce membrane PUFAs, or mutants that confer increased stress responses.