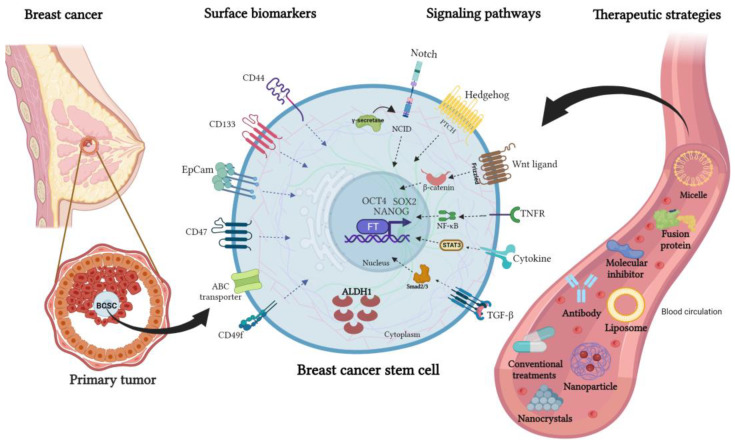
Figure 2.
Surface biomarkers, signaling pathways, and an overview of new therapeutic strategies to target breast cancer stem cells. Mammary CSCs express cell surface proteins that are used as biomarkers such as CD133, CD44, EpCAM, CD47, CD49f, and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. In addition, this cell subpopulation has active signaling pathways, being the main ones Notch, Hedgehog, TGF-β, Wnt/β-catenin, STAT3, PI3K/AKT, and NF-κB. The expression of transcription factors (Nanog, SOX2, and OCT4) allows them to acquire and maintain the characteristics of self-renewal, pluripotentiality, tumorigenic capacity, resistance to therapies, and high metastatic capacity. Several therapeutic strategies have been developed to deliver BCSC-targeted drugs, such as liposomes, micelles, nanoparticles, nanocrystals, and antibodies directed against membrane proteins or inhibitors of BCSC-associated signaling pathways.