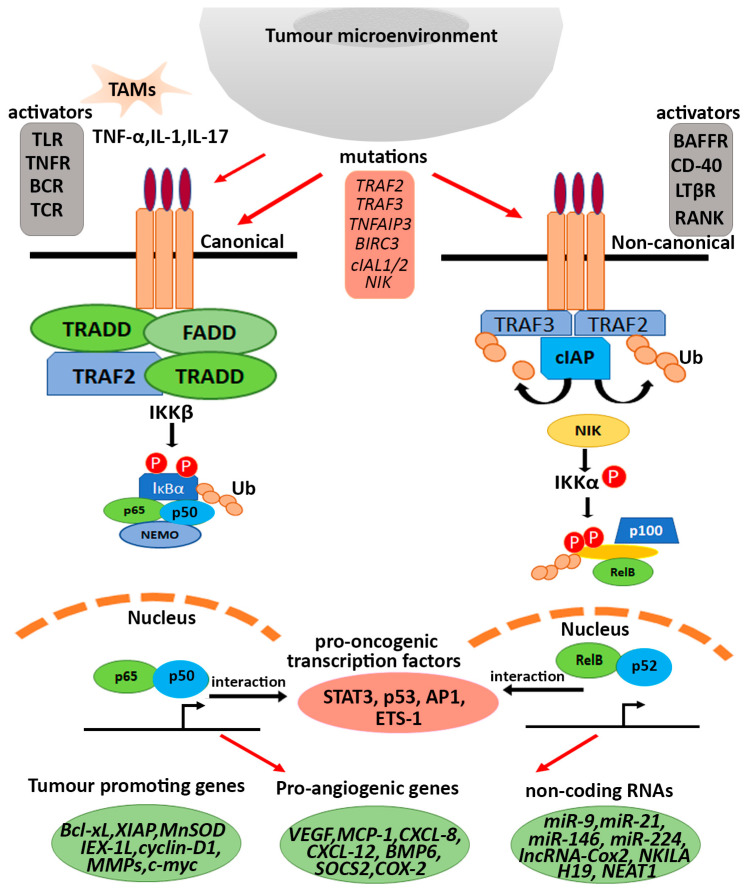
Figure 1.
Aberrant activation and transcriptional regulation of NF-κB pathway in cancer. In addition to constitutive activator molecules of both the canonical and non-canonical NF-κB pathway (highlighted in grey box), activation of the NF-κB pathway in cancer occurs via various other factors involving cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1, IL-17 secreted by tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) and oncogenic driver mutations in various regulatory factors of the pathway (highlighted in pink box). Upon such activation, the activated NF-κB subunits interact with pro-tumorigenic transcription factors (highlighted in red oval), causing activation of alternative target genes associated with tumour promotion phenotypes, angiogenesis and tumour-associated non-coding RNAs.