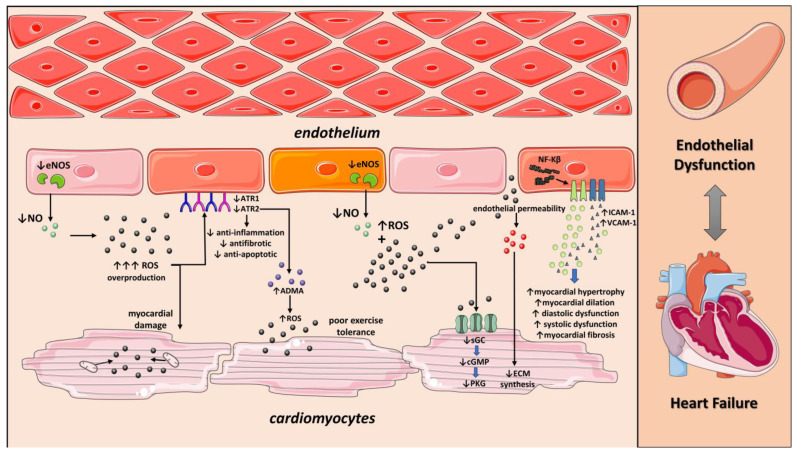
Figure 1.
Role of Endothelial dysfunction on Heart failure. Endothelial dysfunction induces impaired NO production and ROS overproduction. Excessive ROS increases ADMA levels resulting in decreased exercise tolerance. Moreover, ROS production at mitochondria and the presence of dysfunctional antioxidant system cause hypoxia and accelerate myocardial damage. Deterioration of NO-cGMP-PKG pathway increases diastolic dysfunction, myocardial fibrosis, and myocardial hypertrophy. NO: nitric oxide; ROS: reactive oxygen species; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ADMA: Asymmetric Dimethylarginine; ATR1: Angiotensin II receptor type 1; ATR2: Angiotensin II receptor type 2; NF-Kβ: Nuclear factor kappa beta; ICAM-1: Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; sGC: soluble guanylate cyclase; PKG: protein kinase G. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ accessed on 23 of December 2022).