Figure 1.
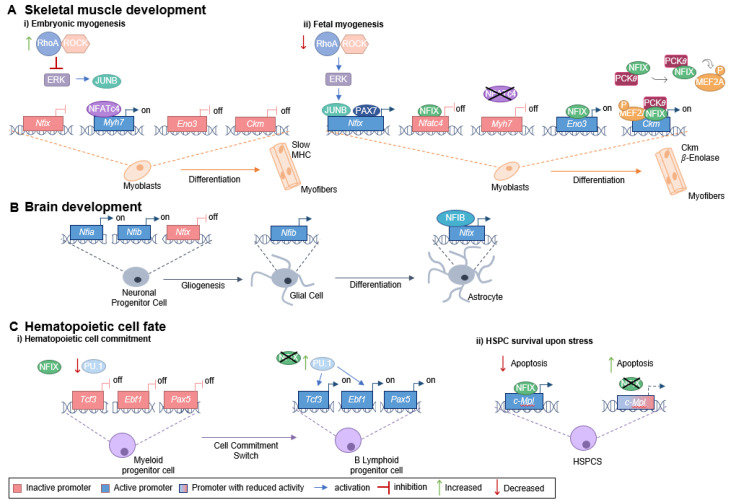
Role of NFIX in development. (A) NFIX promotes the switch between embryonic and fetal myogenesis: (i) During embryonic development, embryonic muscle-specific genes are expressed, including Myh7 (encoding slow MHC), which is activated by NFATc4 that binds to the Myh7 promoter. The RhoA/ROCK axis promotes the embryonic identity of myoblasts through the repression of ERK kinases, JUNB and NFIX. (ii) In the transition from embryonic to fetal muscle development, RhoA/ROCK activity decreases, which leads to increased ERK activity and subsequent activation of JUNB. The transcription factor PAX7 also binds to the Nfix promoter activating its transcription. NFIX binds to the Nfatc4 promotor inhibiting Nfatc4 expression and, consequently, slow MHC is not produced. On the other hand, NFIX activates fetal-specific genes, such as Ckm and Eno3 (which encodes β-enolase), its downstream targets. NFIX binds directly to the Eno3 promoter, activating its transcription, while activation of the Ckm promoter involves a MEF2A/NFIX/PKC𝜃 complex. (B) Glial cell differentiation is promoted by NFIX: the expression of Nfia and Nfib by neuronal progenitor cells leads to a gliogenic switch. Then, NFIB binds the Nfix promoter region activating its transcription, and, in its turn, NFIX activates the astrocytic genes leading to astrocyte differentiation. (C) NFIX regulates hematopoietic cell fate: (i) During a stressful event, NFIX activates the c-Mpl promoter directly, leading to a reduction in the apoptosis of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. (ii) NFIX also prevents early B cell development and favors myeloid differentiation. PU.1 regulates the transcription factors E2A (encoded by Tcf3), EBF (encoded by Ebf1), and PAX5. In the presence of NFIX, PU.1 levels are lower, and therefore, the expression of Tcf3, Ebf1, and Pax5 decreases, favoring myeloid fate. When NFIX is absent, the expression of PU.1 increases, enabling the activation of key genes required for B cell lymphoid lineage commitment (Tcf3, Ebf1, and Pax5).