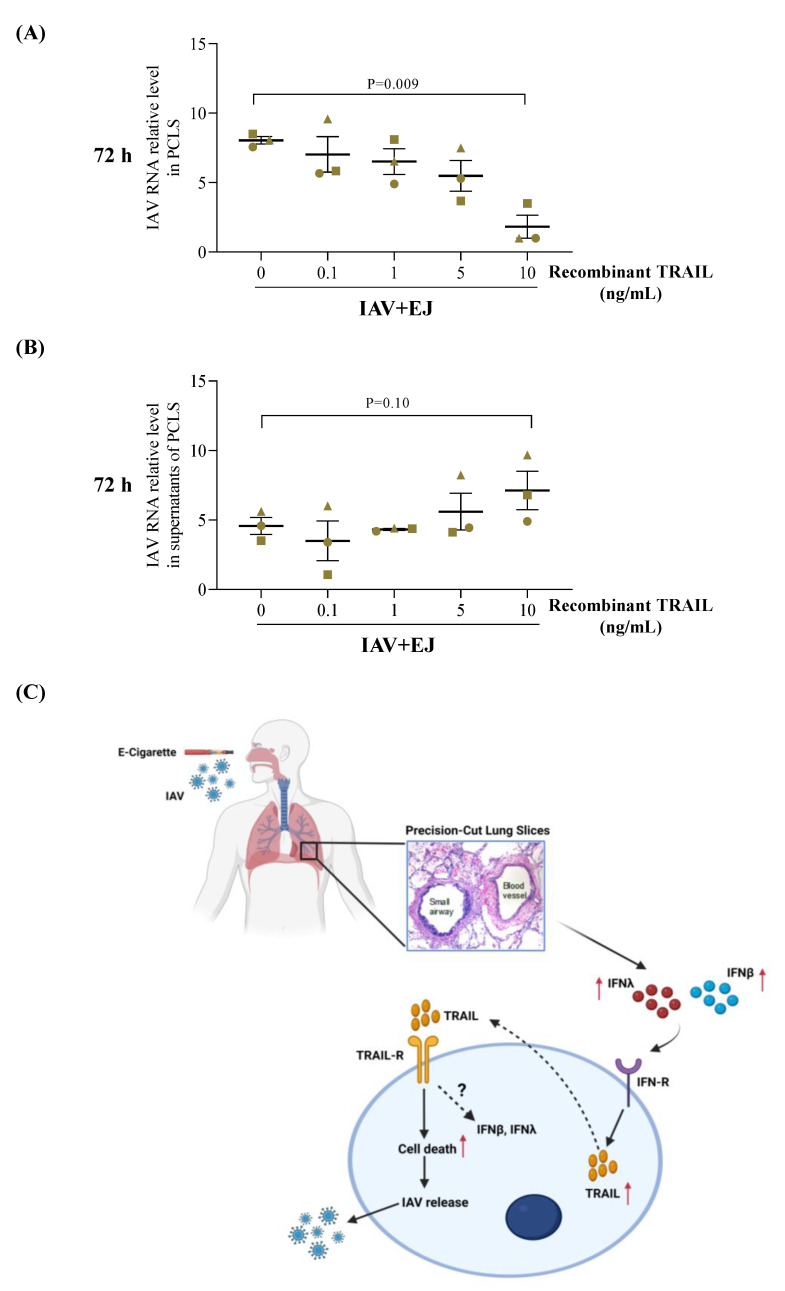
Figure 6.
The dosing effect of recombinant TRAIL on viral infection in human precision-cut lung slices (PCLS) treated with E-juice (EJ) and influenza A virus (IAV). PCLS were treated with IAV and EJ in the presence or absence of BSA (control) and recombinant TRAIL (0.1–10 ng/mL) for 72 h. IAV load in tissue (A) and supernatants (B) was analyzed by RT-PCR. Each data point represents the individual replicate from a single donor. Horizontal lines indicate mean ± SEM. Paired t-test was used to analyze the data (C) Proposed mechanisms by which electronic cigarette (E-cig) exposures regulate IAV infection in human distal lungs. E-cig exposures amplify the expression of IFN-β and IFN-λ induced by IAV infection, which may upregulate TRAIL release. TRAIL binds to the TRAIL receptors to initiate cell apoptosis to enhance the release of IAV from the infected tissue. As a feedback loop mechanism, TRAIL may also upregulate the expression of IFN-β and IFN-λ to serve as an additional host defense mechanism.