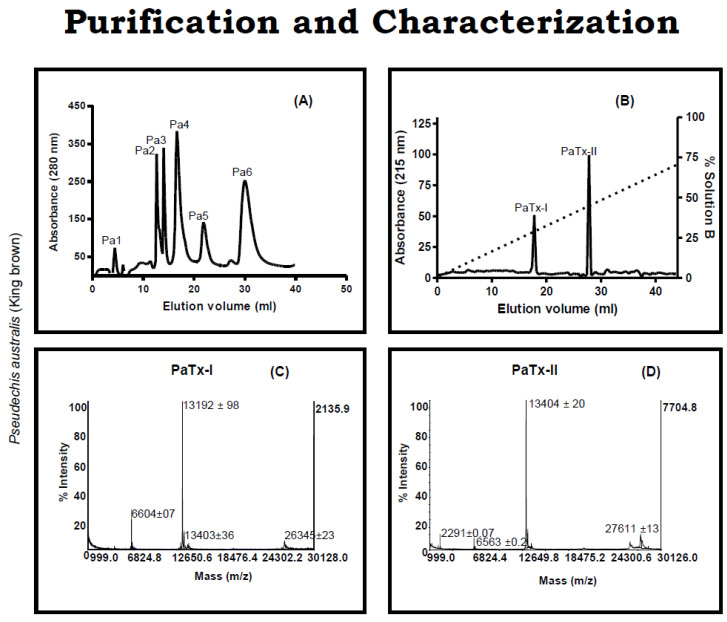
Figure 1.
Purification and characterization of snake venom proteins. (A) Six fractions (Pa1–Pa6) were separated from the crude venom of P. australis (king brown) by a Superdex G-75 column equilibrated with 50 mM Tris-HCL buffer (pH 7.4). (B) The fractions (Pa4) containing antibacterial and PLA2 activities were further purified by reverse-phase (RP)-HPLC on C18 and resolved into six peaks (Pa-F1 to Pa-F6). The most active peak (Pa-F2) was further separated on a C8 column, producing two pure proteins, PaTx-I and PaTx-II. (C,D) Molecular weights of the svPLA2 proteins (PaTx-I and PaTx-II) were determined using MALDI-TOF/MS.