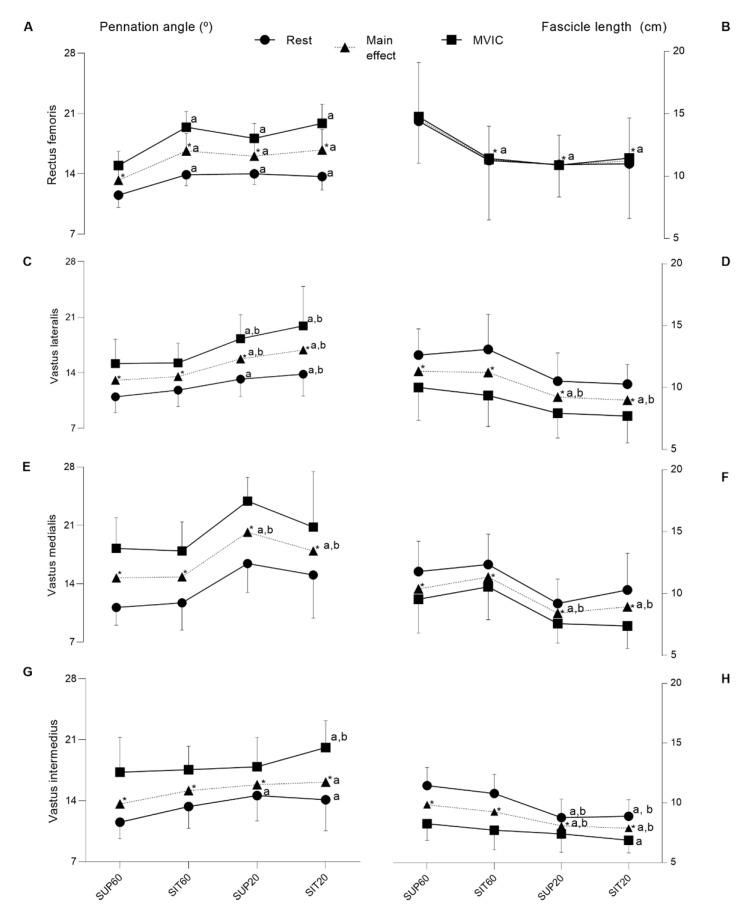
Figure 5.
The pennation angle and fascicle length of the quadriceps femoris constituents according to hip and knee angles during rest and contraction. Muscle (left y-axis) and different conditions (right x-axis). Rest (closed circle line), main effect (closed triangle line) and during MVIC (closed square line). The first column (pennation angle—θp (°) and second column (fascicle length—Lf (cm)). Data are presented as means and confidence intervals (CI 95%). (A,B) Rectus femoris; (C,D) Vastus lateralis; (E,F) Vastus medialis; (G,H) Vastus intermedius. Legend: SUP60: supine with 60° of knee flexion; SIT60: seated with 60° of knee flexion; SUP20: supine with 20° of knee flexion; SIT20: seated with 20° of knee flexion; θp: pennation angle; Lf: fascicle length. Significant differences: a different from SUP60 at (p ≤ 0.05); b different from SIT60 (p ≤ 0.05); * indicate significant differences in intensity (p ≤ 0.05) between rest and MVIC.