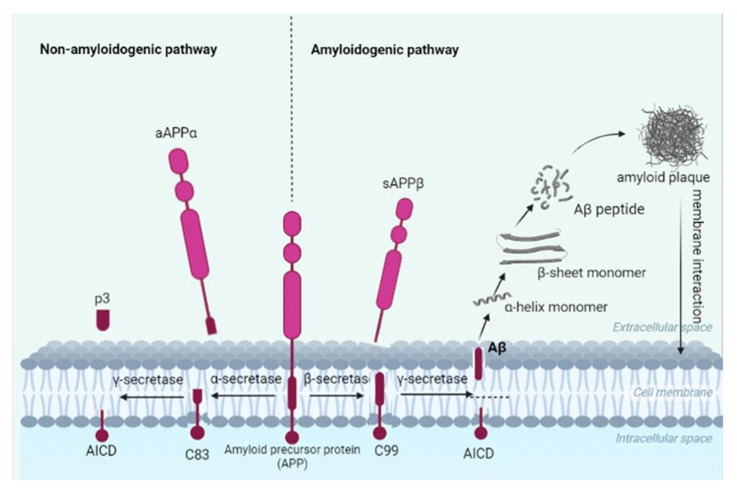
Figure 2.
Non-amyloidogenic and amyloidogenic pathways of amyloid precursor protein (APP) cleavage. The non-amyloidogenic pathway leads to the formation of an 83-amino acid fragment (a CTFα), which, when treated with γ-secretase, forms a two-fragment p3 and AICD, being an APP intracellular domain. These forms are not toxic and are not able to form senile plaques. The amyloidogenic pathway, however, is a toxic form of APP cleavage and leads to the formation of a soluble aAPPβ fragment and a C-terminal part composed of 99 amino acids. The latter, under γ-secretase activity, creates Aβ, which is able to aggregate towards senile plaques.