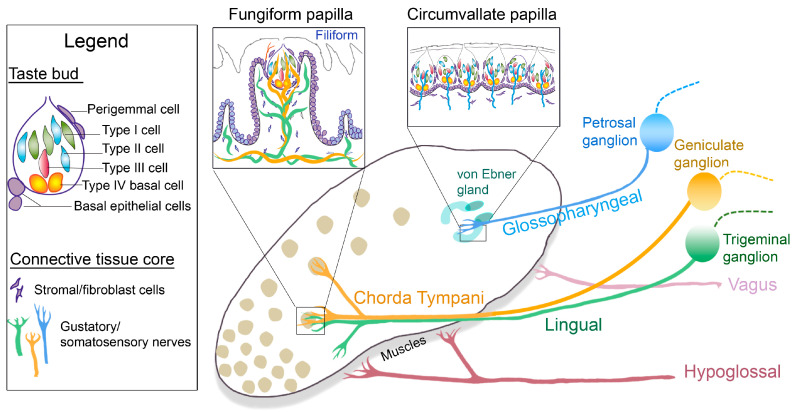
Figure 1.
Anterior and posterior tongue papillae and nerves: Diagram of the tongue dorsum illustrating the taste organs, multiple fungiform (rounded) and single circumvallate (U-shaped) papillae on the anterior and posterior tongue, respectively. Minor salivary von Ebner glands, associated with circumvallate papillae, are labelled in the posterior tongue. The gustatory nerves, chorda tympani (yellow) and glossopharyngeal (blue), project from the corresponding sensory ganglia, geniculate and petrosal, respectively, to the anterior and posterior papilla taste buds. The somatosensory lingual nerve (green) fibers derive from the trigeminal ganglion, enter the anterior tongue together with the chorda tympani, and are within the connective tissue core of the Fungiform and non-gustatory Filiform papillae. The central projections of these nerves from the ganglia are represented in dashed lines. Hypoglossal and vagus motor fibers innervate the extrinsic and intrinsic tongue muscles and the posterior palatoglossus muscles. The boxed diagrams are as follows: The fungiform papilla, surrounded by non-taste filiform papillae, includes a single apical taste bud and a broad connective tissue core with stromal cells and innervation. The circumvallate papilla has numerous taste buds aligned next to each other in the epithelium with innervation and stromal cells in the connective tissues. The legend includes taste bud cell types (Type I, II, and III), taste bud progenitors (Type IV basal cells, perigemmal cells, and basal epithelial cells), and elements of the connective tissue core.