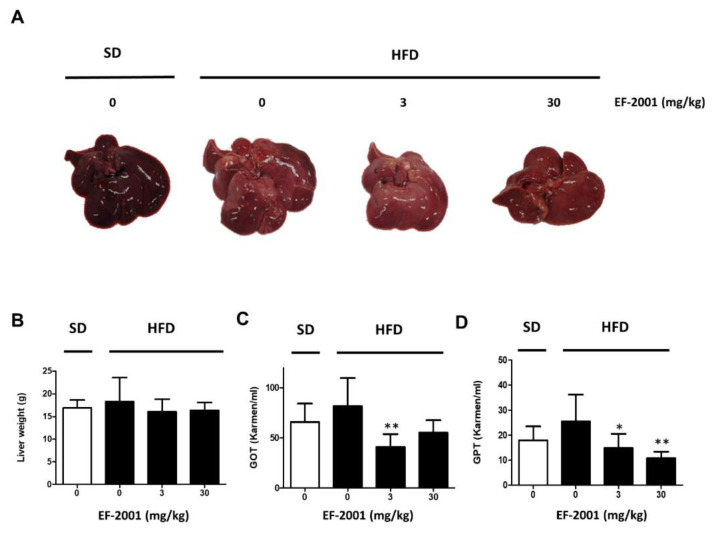
Figure 1.
Effects of EF-2001 oral administration on high fat diet (HFD)-induced accumulation of liver tissue and level of glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase/glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GOT/GPT) in serum of obese rats. Male rats were divided into standard diet (SD) or HFD groups and were orally administered refined water or 3 mg/kg or 30 mg/kg EF-2001 in water (n = 6 rats/group). Gavage was continued for 6 weeks. After six weeks of feeding, rats were fasted for 12 h, and then, blood samples were collected. (A) Effects of EF-2001 on the accumulation of liver tissue of HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. Pictures were taken for livers of each group. (B) Effects of EF-2001 on the liver weight of rats fed SD and HFD for 6 weeks. To investigate the weight of liver tissue, the rats were sacrificed, and liver tissue weight was measured. (C) Effects of EF-2001 on GOT in HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. (D) Effects of EF-2001 on GPT in HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. Data was analyzed with liver tissue weight per body weight. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. (n = 6); * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. HFD-fed rats alone without EF-2001.