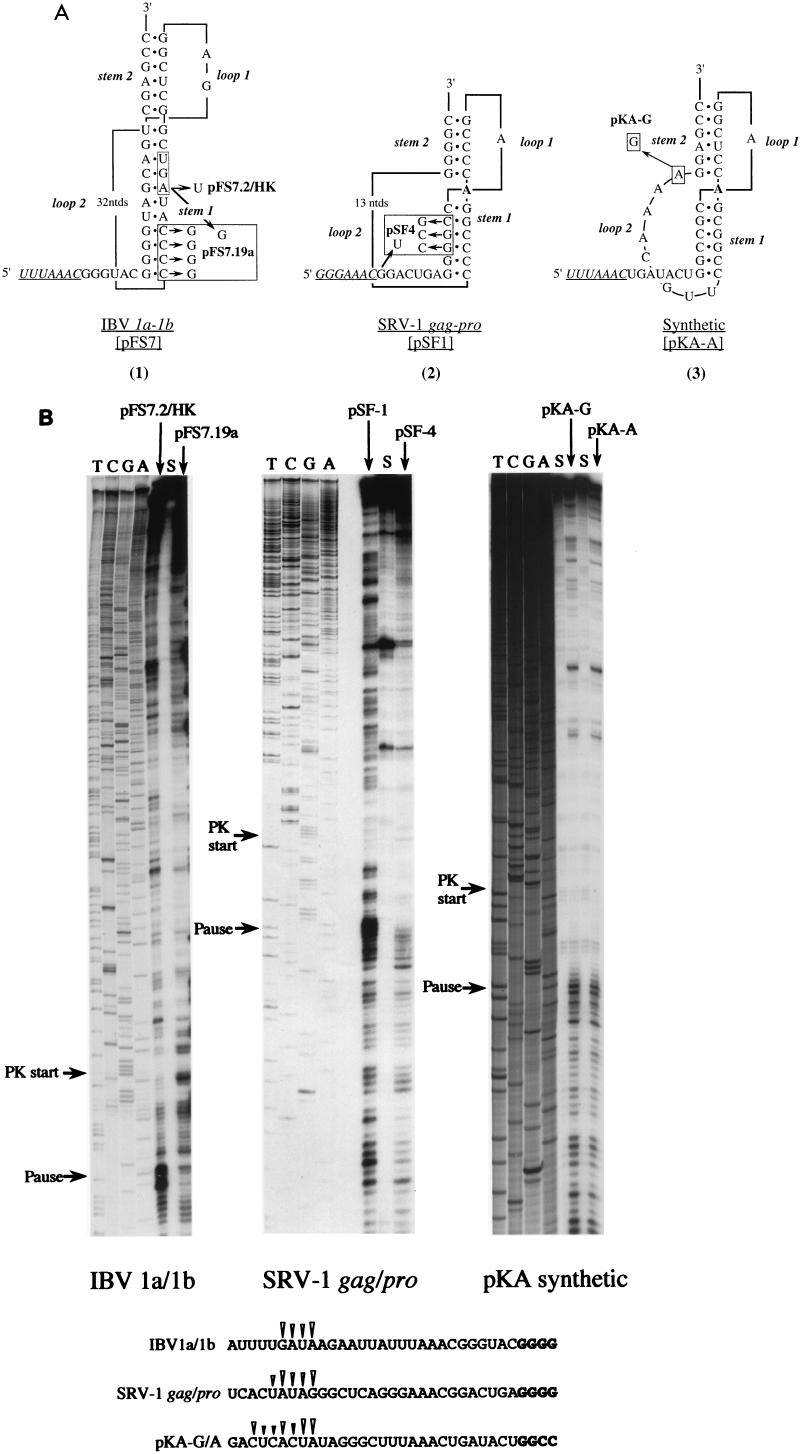
FIG. 4.
Ribosomal pausing at natural and synthetic frameshift signals. (A) Predicted secondary structures of natural and synthetic frameshift signals tested in heelprint assays (1). Plasmid pFS7 contains the wild-type IBV slippery sequence (UUUAAAC, underlined) and pseudoknot (2). The 1a termination codon (UGA), which forms part of stem 1, is boxed. Plasmids pFS7.2/HK and pFS7.19a are mutant derivatives in which the 1a termination codon has been changed to UGU or UGG, respectively. Plasmid pFS7.19a contains an additional mutation, a complementary change that destabilizes stem 1 of the pseudoknot (2). Plasmid pSF1 contains the SRV-1 gag/pro frameshift region (42). A derivative, pSF4, has a destabilizing mutation in stem 1 and, additionally, a termination codon (UGA) immediately downstream of the slippery sequence (GGGAAAC, underlined). The unpaired A residue (in bold) between the stems is drawn on the basis that the pseudoknot is similar to that of MMTV gag/pro (see text). Recent NMR studies have challenged this belief (14, 29) and suggest that the A is in fact paired with the most 3′ base of loop 2 (a U). The synthetic frameshift site pKA-A (25) has an IBV-like slippery sequence (UUUAAAC, underlined) and an MMTV-like stimulatory pseudoknot. Plasmid pKA-G differs solely in the identity of the last residue of loop 2. (B) mRNAs from SmaI-digested pFS7.2/HK and pFS7.19a or BamHI-digested pSF-1, pSF-4, pKA-A, and pKA-G were subjected to heelprint analysis as detailed in Materials and Methods. Heelprints of each RNA are shown alongside a sequencing ladder (TCGA) prepared from the relevant plasmid. Each reaction mixture contained 20 ng of the relevant single-stranded DNA template, 0.4 ng of primer, and 3 μl of RPFs. Lanes marked S indicate heelprints in which RPFs were replaced by an equivalent amount (vol/vol) of material harvested from the supernatant produced in the airfuge centrifugation step (see Materials and Methods). The start of each pseudoknot and the position of pseudoknot-dependent ribosomal pauses are indicated by arrows. The primary sequences of the mRNA upstream of the various pseudoknots are shown at the bottom and the position of the pseudoknot-dependent heelprints are indicated with arrowheads (the first four pseudoknot residues are shown in bold type in each case).