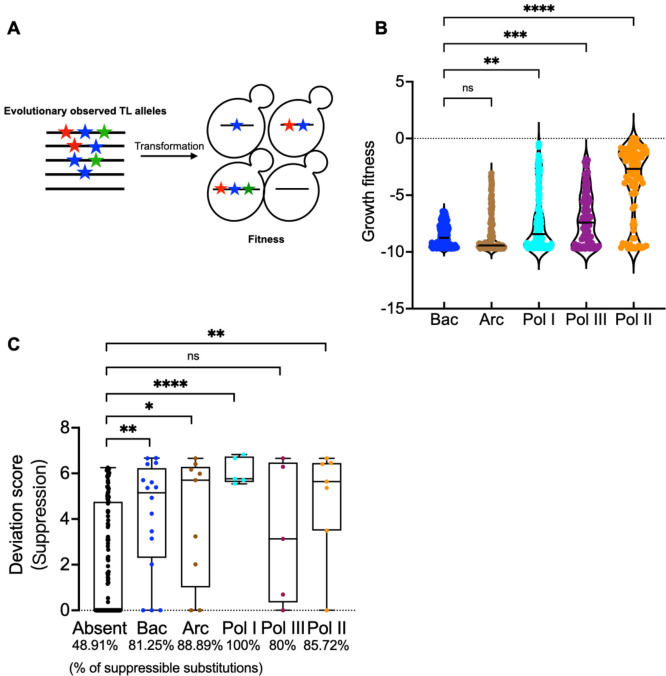
Figure 5. Contextual epistasis shapes TL evolution.
A. Schematic for the TL evolutionary haplotypes library. We selected 662 TL haplotypes representing TL alleles from bacterial, archaeal and the three conserved eukaryotic msRNAPs. These TL alleles were transformed into yeast and were phenotyped under selective conditions. B. Fitness of evolutionarily observed TL haplotypes in the yeast Pol II background. The Pol II WT TL fitness (0) is labeled as dotted line. Kruskal-Wallis test was performed for comparison and significant levels (P < 0.05) were labeled. C. A comparison of the maximum deviation score of each TL lethal single substitution that is present in any evolutionary TL haplotypes from bacterial, archaeal or eukaryotic Pols versus those that have not been observed in any species. The evolutionary TL haplotypes were from multiple sequence alignments (MSA). 9 substitutions were found in an MSA of 542 archaeal TL sequences that are lethal when present in yeast as a single substitution. 17 were found in an MSA of 1403 bacterial TLs, 5 were found in 749 Pol I TLs, 7 were found in 499 Pol II TLs, and 5 were found in 539 Pol III TLs. Evolutionarily observed lethal substitutions were compared to those unobserved in our TL MSA. The percentage of in total suppressible lethal single mutants for each group is labeled at the bottom of the plot. Statistical comparison was done with the Mann-Whitney test and the significant levels (P < 0.05) are shown in the figure.