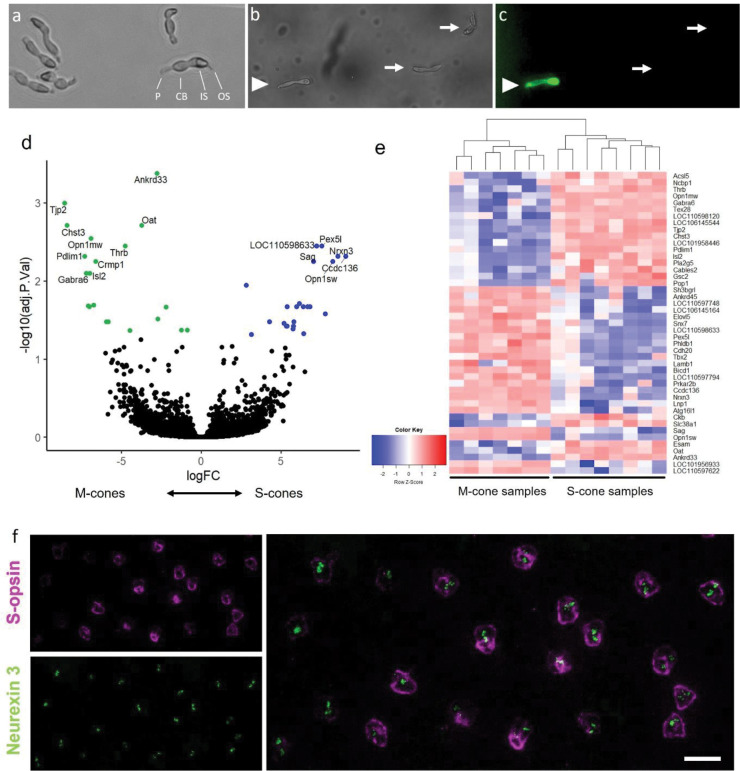
Figure 1.
SMART-seq approach on manually collected M- and S-cone samples. a) Cones after dissociation. P: pedicle, CB: cell body, IS: inner segment, OS: outer segment. b-c) Fluorescently labeled live cones after antibody incubation under bright field (b) and excitation light (c) conditions. Labeled cone (arrowhead) was categorized as S-cone, while cells with cone morphology but without label (arrows) were categorized as M-cones. d)-e) Differentially expressed genes in S-and M-cone photoreceptors. d) Volcano plot highlighting significant genes enriched in M-cones (logFC < 0) and S-cones (logFC > 0). e) Heat map showing expression of significant differentially expressed genes in all samples. f) Validation of cone subtype-specific gene expression of Nrxn3. Flat-mounted ground squirrel retina after fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) with Nrxn3-probe, followed by S-opsin antibody-staining. Magenta: anti-S-opsin antibody. Green: Nrxn3 FISH probe. Scale bar: 10 μm.