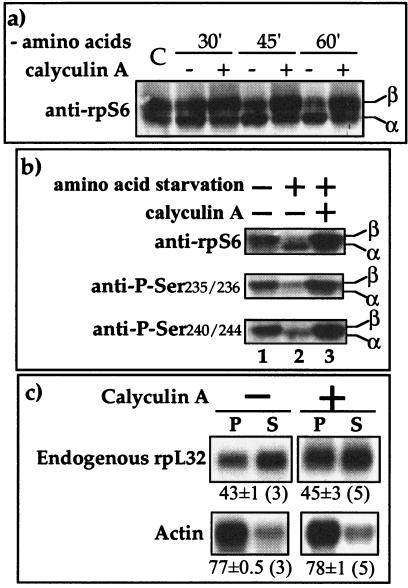
FIG. 4.
Calyculin A induces phosphorylation of rpS6 but fails to relieve the translational repression of TOP mRNAs. (a) 293 cells were either untreated (C) or amino acid starved without (−) or with (+) calyculin A (20 nM) for the indicated time, after which cells were harvested. The cytoplasmic proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-rpS6. α and β, unphosphorylated and hyperphosphorylated forms of rpS6, respectively. (b) 293 cells were untreated or amino acid starved for 1 h without (−) or with (+) calyculin A (20 nM), after which cells were harvested. The cytoplasmic proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. (c) 293 cells were amino acid starved for 1 h without (−) or with (+) calyculin A (20 nM) and then harvested, and the polysomal distribution of the mRNAs encoding rpL32 and actin was analyzed and presented as described in the legend to Fig. 2.