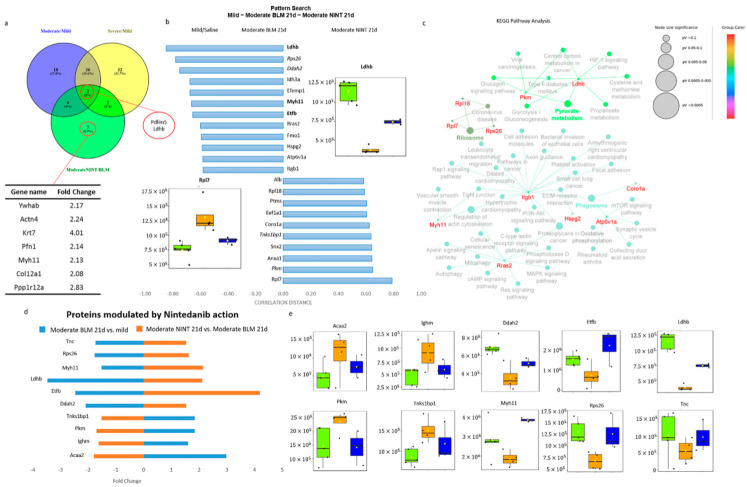
Figure 5.
Nintedanib-mediated fibrosis slowdown. (a) Venn diagram comparing statistically significant proteins (p-valueadj ≤ 0.05, Fold Change ≥ 2 or ≤−2) in the comparisons of moderate BLM vs. mild/ severe BLM vs. mild/moderate NINT 21d vs. moderate BLM 21d; the two proteins common to all pairwise comparison are circled in red; and the even proteins are statistically significant (p-valueadj ≤ 0.05, fold change ≥ 2 or ≤−2) only in the comparison moderate NINT 21d vs. moderate BLM 21d are listed in a table. (b) Pattern search analysis of the proteins with a statistically significant (p-value ≤ 0.05) correlation pattern and modulated (increased or decreased) by NINT treatment in the comparison between mild (green), moderate BLM 21d (orange), and moderate NINT 21d (blue), the correlation distance value in the bar chart is expressed based on the pattern search 1-2-1. (c) Cytoscape network of KEGG pathways obtained including the analysis of all 22 proteins with a statistically significant correlation. (d) Ten proteins with a reversing fold change in the comparison between moderate-BLM 21d vs. mild and moderate-NINT 21d vs. moderate-BLM 21d (p-valueadj ≤ 0.05, FC ≥ 1.5 or ≤−1.5). (e) Boxplots of the ten proteins. In all boxplots, mild/saline boxes are colored in green, moderate BLM 21d in orange, and moderate NINT 21d in blue. BLM—bleomycin; NINT—nintedanib; and d—days. In all Boxplots, black dots represent the abundance of the selected features in all samples, yellow diamond represents the mean abundance.