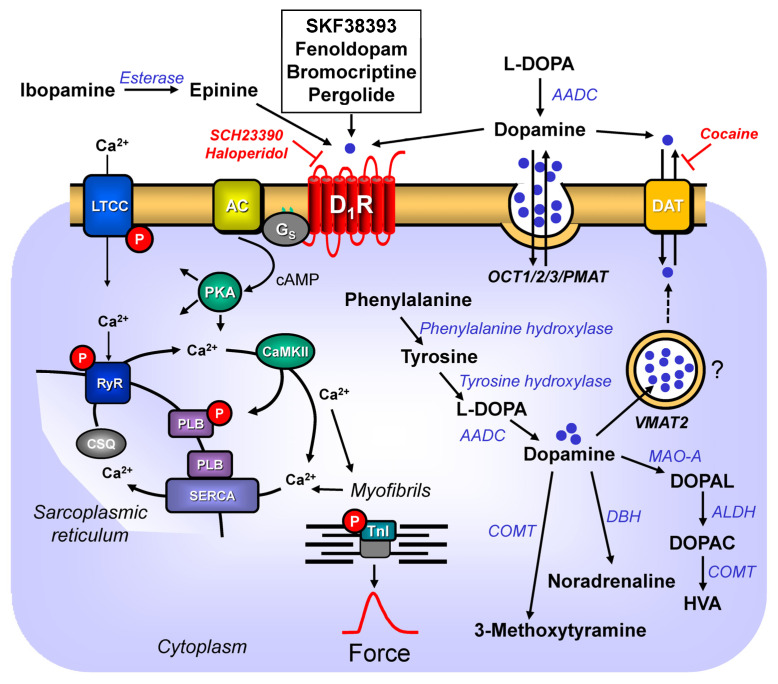
Figure 1.
Dopamine might stimulate D1-dopamine receptors in the sarcolemma. This would activate the stimulatory GTP-binding protein (Gs), and thereby, the activity of adenylyl cyclases (AC) would be enhanced. AC will catalyze the conversion of ATP to cAMP. This cAMP can activate cAMP-dependent protein kinases (PKA), leading to an increase in the phosphorylation states of regulatory proteins. For instance, phosphorylation of L-type Ca2+ channels (LTCC) will lead to more of an influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular space. This Ca2+ will facilitate the release of Ca2+ through the phosphorylated ryanodine receptor (RYR) into the cytosol. The cytosolic Ca2+ activates a Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMKII) that can phosphorylate phospholamban (PLB), the inhibitory protein of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA). Possibly, dopamine can also be synthesized in cardiomyocytes. Phenylalanine is oxidized by phenylalanine hydroxylase to tyrosine. Tyrosine is in due course oxidized by tyrosine hydroxylase to L-DOPA, and aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) forms dopamine. Dopamine can be oxidized by dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH) to noradrenaline. Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) forms 3-methoxytyramine. Monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) will oxidize dopamine to dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) to dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), and finally, COMT will form homovanillic acid (HVA). Dopamine, at least in nerve cells, can be transported by a vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2) into vesicles. These vesicles can release dopamine to the extracellular space. Dopamine can enter the cell via a dopamine transporter (DAT) or via other transporters (OCT, organic cation transporter; PMAT, plasma membrane monoamine transporter). Additionally, the D1-dopamine receptor can also be stimulated (see Table 1A) by fenoldopam, SKF38393, bromocriptine, pergolide, and possibly epinine. Epinine is formed from ibopamine through the activity of esterases. The D1-dopamine receptor will be blocked by haloperidol, but also by SCH23390 (see Table 1B).