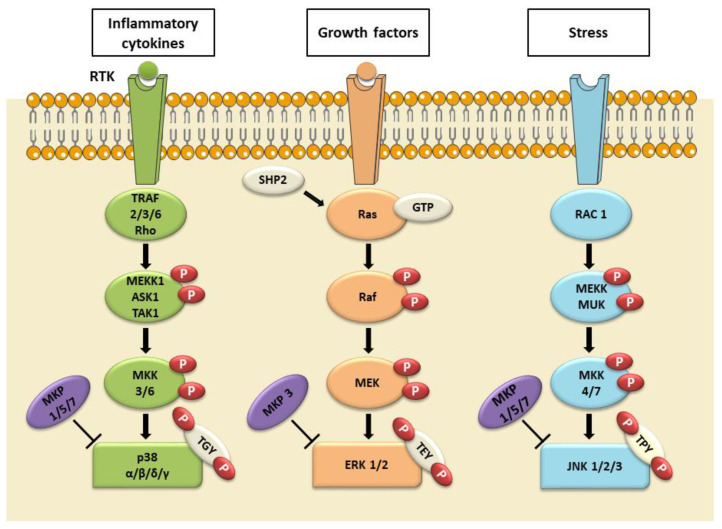
Figure 2.
The MAPK signaling pathways. In mammalian cells, there are three well-known MAPK pathways: the ERK1/2, the c-JUN N-terminal kinase 1, 2, and 3 (JNK1/2/3), and the p38 α, β, δ, and γ MAPK pathways. ERK1/2 is activated in response to growth factors, hormones, and proinflammatory stimuli, while JNK1/2/3 and p38 α, β, δ, and γ are activated by cellular and environmental stresses, in addition to pro-inflammatory stimuli. The image was created using the image bank of Servier Medical Art (Available online: http://smart.servier.com/, accessed on 30 December 2022), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/, accessed on 30 December 2022). Mitogen-activated protein kinases: MAPKs; c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1, 2, and 3: JNK1/2/3; extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2: ERK1/2; MAPK phosphatases 1, 3, 5, 7: MPK1/3/5/7; tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor: TRAF; SH2 containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2: SHP2; Guanosine-5′-triphosphate: GTP; Rac Family Small GTPase 1: RAC1; MEK kinase 1: MEKK1; Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1: ASK1; transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1: TAK1; MAPK upstream kinase: MUK; MAP kinase kinase 3, 4, 6 and 7: MKK3/4/6/7; Thr-Gly-Tyr motif: TGY; Thr-Glu-Tyr motif: TEY; Thr–Pro–Tyr motif: TPY; receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK).