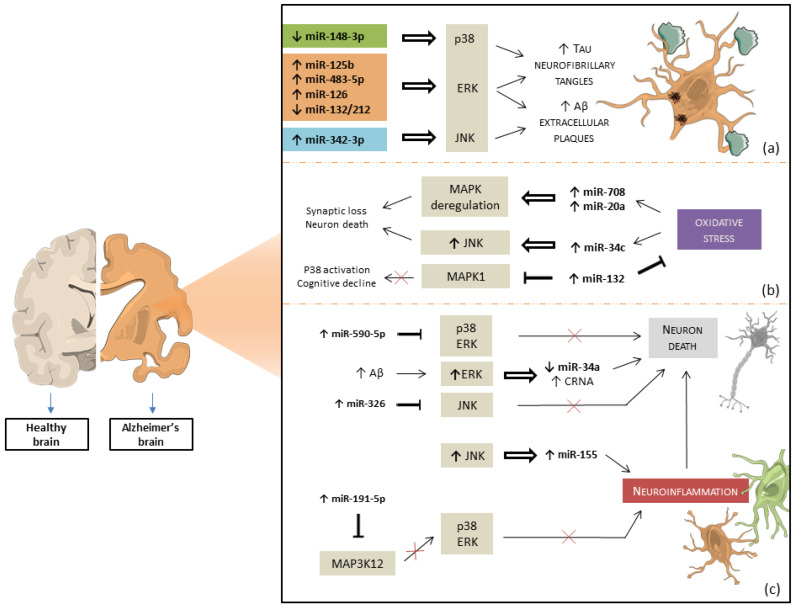
Figure 3.
miRNAs and MAPKs interaction in Alzheimer’s disease. (a) The overexpression or the downregulation of miRNAs can act on p38 MAPK, JNK, and ERK in a direct or indirect way, exacerbating NFT and amyloid extracellular plaques in AD neurons. (b) Oxidative stress enhances miRNAs expression during AD, causing deregulation in the MAPK pathway and, consequently, synaptic and neuron loss. The overexpression of miR-132 decreases oxidative stress, p38 MAPK, and cognitive decline by targeting MAPK1. (c) The Aβ depositions induce ERK activation, which leads to a decrease in miR-34a expression levels and, thus, to neuronal death due to the CRNA. The overexpression of miR-590-5p and miR-326 plays an anti-apoptotic effect through indirect inhibition of p38 MAPK, ERK, and JNK activation. JNK mediates downstream miR-155 upregulation and promotes neuroinflammation during AD. The overexpression of miR-191-5p reduces microglia injury through the decrease in p38 MAPK and ERK activity by targeting the upstream MAP3K13 effector. Neuroinflammation plays an important role in the onset and progression of neurodegeneration and neuronal loss in neurodegenerative diseases. The image was created using the image bank of Servier Medical Art (Available online: http://smart.servier.com/, accessed on 30 December 2022), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/, accessed on 30 December 2022). microRNAs: miRNAs; Mitogen-activated protein kinases: MAPKs; c-JUN N-terminal kinase: JNK; extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERK; Neurofibrillary tangles: NFT; Alzheimer’s disease: AD; Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 1: MAPK1; reactive oxygen species: ROS; amyloid-β: Aβ; Transcription factor Jun: c-Jun; Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 12: MAP3K12; cell cycle-related neuronal apoptosis (CRNA).