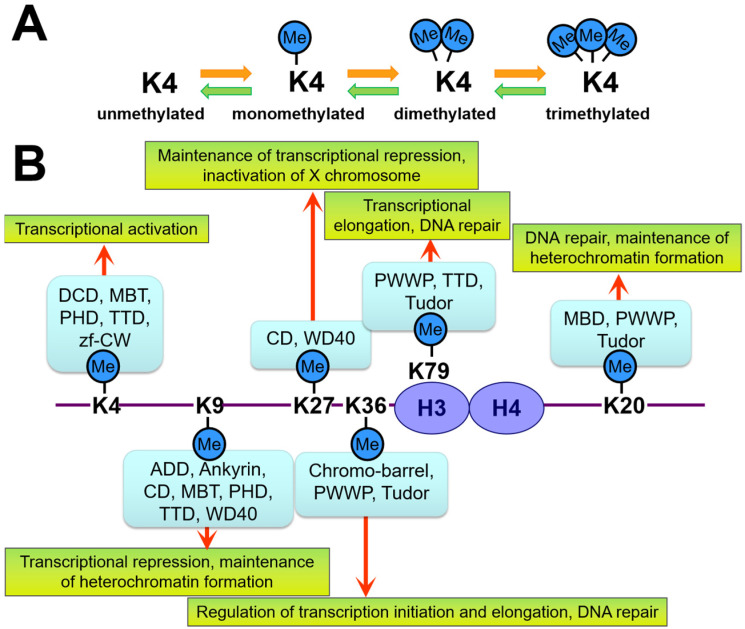
Figure 1.
Schematic showing how lysine (K) methylation (Me) is recognized by different domains of “reader” proteins and their outcomes. (A) Each lysine residue on the histone can either be mono-, di-, or trimethylated. Each of these post-translational modifications is recognized by different “reader” proteins. (B) Methylation of lysine residues of H3 and H4 and the protein domains that recognize them. The binding proteins, and not histone modification, change the chromatin structure. ADD—Alpha-thalassemia intellectual disability syndrome X-linked (ATRX)-DNMT3-DNMT3L; CD—chromodomain; MBD—methyl-lysine-binding domain; MBT—malignant brain tumor; PHD—plant homeodomain; PWWP—conserved Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro motif; TTD—tandem Tudor domain; zf-CW—zinc-finger CW.