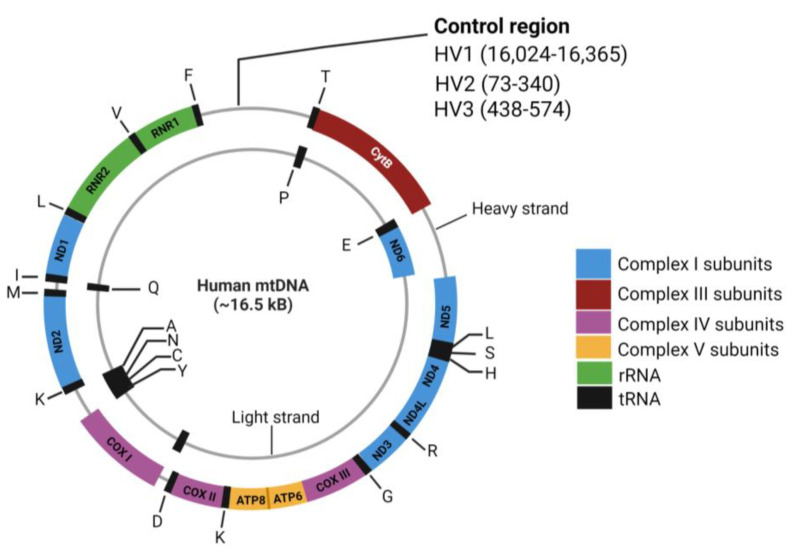
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial genome. Mitochondrial respiratory complex function is maintained by both nDNA- and mtDNA-encoded genes. The transcripts of the nDNA-encoded respiratory complex subunits are translated in the cytoplasm and imported into the mitochondria through the mitochondrial import machinery. Thirteen protein-coding genes in mt genome belong to various respiratory complexes (I: ND1, ND2, ND3, ND4, ND4L, ND5, and ND6); III: CYTB, IV: COXI, COXII, COXIII, and V: ATP6 and ATP8). The noncoding portion of mt genome consists of rRNA and 22 tRNA genes that are important for translation of the mtDNA-encoded transcripts. The control region, sometimes referred to as the D-loop, consists of three hypervariable segments termed HV1, HV2, and HV3. This region also contains replication initiation sites and promoter regions for transcription of the two mtDNA strands. Figure was created with BioRender.com (accessed on 19 February 2023).