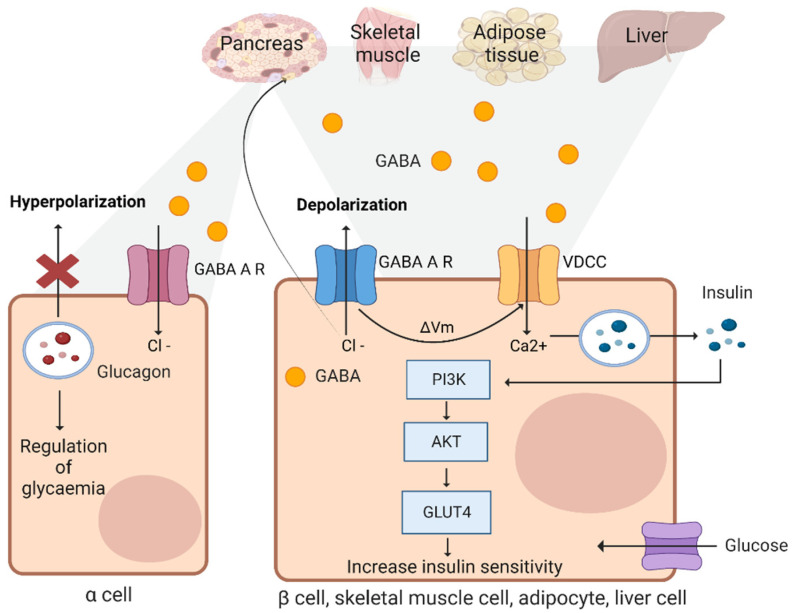
Figure 2.
The function of GABA in various organs. Schematic representation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on transmission in the pancreas, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and liver. GABA induces hyperpolarization in alpha cells in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas by increasing the inflow of Cl−. The membrane hyperpolarization inhibits the action of glucagon secretion. GABA regulates glycemia by inhibiting alpha-cell function. On the other hand, GABA induces depolarization in beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, skeletal muscle, adipocyte, and liver cells, by increasing the inflow of Ca2+. In this case, GABA activates the PI3K-AKT pathway to increase insulin sensitivity by upregulating glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) expression.