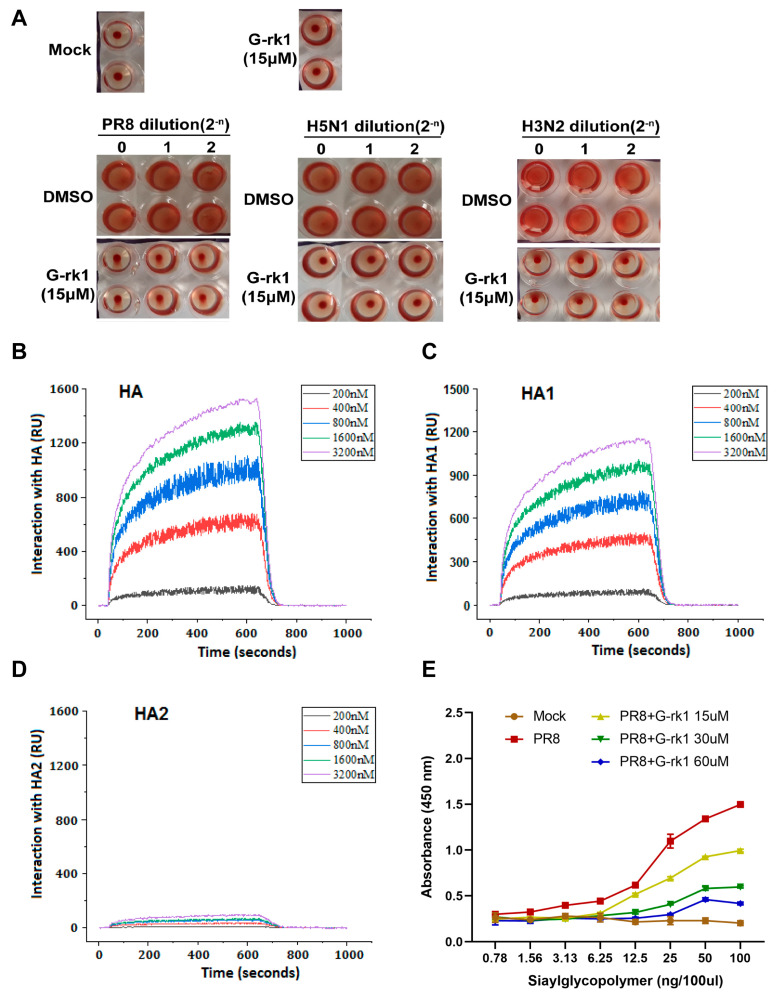
Figure 4.
Identifying HA as the potential target of G-rk1. In (A), an HAI assay using 2-fold serially diluted A/Puerto Rico/8/34 (PR8, H1N1), A/Duck/Guangdong/212/2004 (H5N1), and A/Guangdong/Dongguan/1100/2006 (H3N2) viruses (staring at 16 HA units) and 1% CRBCs was performed in the absence or presence of G-rk1. In (B–D), HA or HA1 or HA2 from PR8 virus was immobilized on a photo-cross-linker sensor chip. Subsequently, G-rk1 was injected as an analyte at various concentrations, and PBST was used as the running buffer. The interaction signals were retrieved and analyzed with bScreen LB 991 software. The affinities of the interactions between G-rk1 with HA, HA1, and HA2 are shown in (B–D), respectively. In (E), PR8 virus (64 HA units) was treated with or without G-rkl for 2 h at 37 °C and then added into the plate coated with Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ-PAA-biotin (3′-SLN) at 4 °C for 12 h. The plate was then incubated with mouse monoclonal antibody against HA protein of H1 subtype at 4 °C for 3 h, and then washed with PBST and incubated with HPR-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG for 2 h at 4 °C. The absorbance values were read at 450 nm.