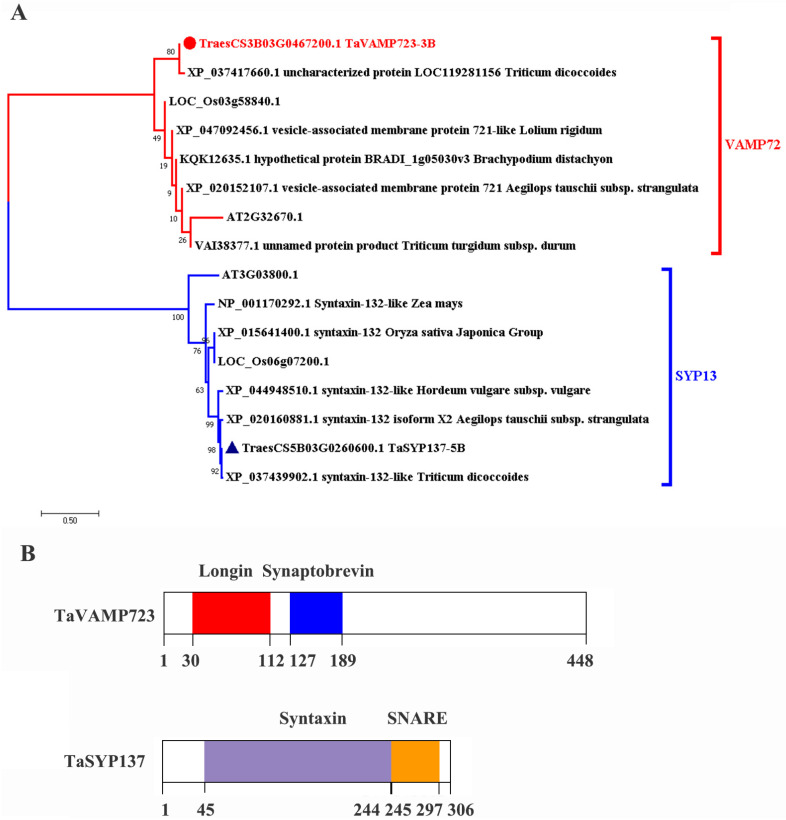
Figure 1.
Analysis of TaVAMP723-3B and TaSYP137-5B. (A): Phylogenetic analysis of TaVAMP723 and TaSYP137 was conducted by constructing a phylogenetic tree using the maximum likelihood method with MEGA X software. Different SNARE proteins from Triticum aestivum (TaVAMP723-3B, TaSYP137-5B), Arabidopsis thaliana (AT2G32670.1, AT3G03800.1), Oryza sativa (LOC_Os03g58840.1, LOC_Os06g07200.1, XP_015641400.1), Triticum turgidum (VAI38377.1), Aegilops tauschii (XP_020152107.1, XP_020160881.1), Brachypodium distachyon (KQK12635.1), Lolium rigidum (XP_047092456.1), Triticum dicoccoides (XP_037417660.1, XP_037439902.1), Hordeum vulgare (XP_044948510.1), and Zea mays (NP_001170292.1). Red branches represent VAMP72-like proteins; Blue branches represent SYP13-like proteinsThe two wheat proteins TaSYP137 and TaVAMP723 are marked with blue triangle and red circles, respectively. The number on the evolutionary branches indicates the BOOTSTRAP value, and a value of 100 indicates that the probability of this branch is 100%. (B): The functional domains predicted by Pfam. TaVAMP723-3B has the longin domains (30 aa-112 aa) and synaptobrevin domains (127 aa-189 aa), while TaSYP137-5B contains the syntaxin domains (45 aa-244 aa) and SNARE domains (245 aa-297 aa).