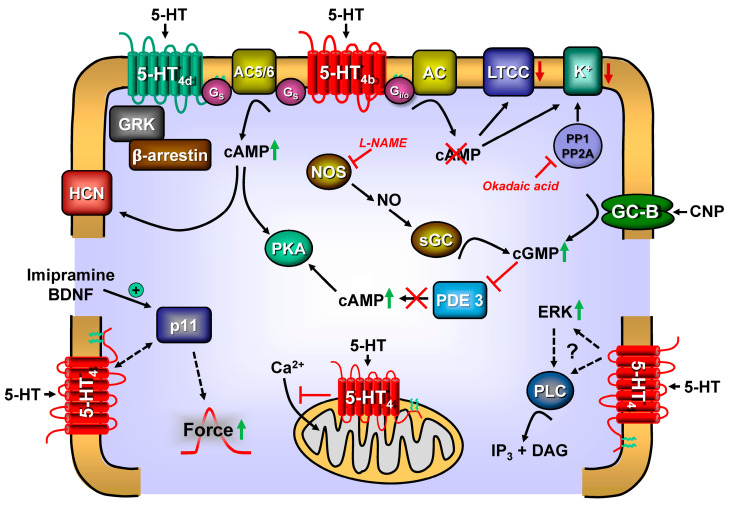
Figure 2.
Synopsis of putative signal transduction of 5-HT4-receptors in the heart. For general information and abbreviations, see Figure 1. 5-HT4a-receptors couples only via stimulatory G-proteins (Gs). 5-HT4b-receptors couple via both Gs and inhibitory G-proteins (Gi). The 5-HT4-receptors can signal via guanosine triphosphate–protein couple receptor kinases (GRK). The 5-HT4-receptors can be phosphorylated and inactivated via GRK. The cAMP can bind and activate a hyperpolarisation-activated cation-channel (HCN), inducing tachycardia in the sinus node of the heart. Moreover, imipramine or BDNF treatment increase the expression of PIN1. Augmented levels of PIN1 can facilitate the coupling of 5-HT4-receptors to force generation. The coupling of 5-HT4-receptors to potassium channels (K+) is activated by PKA and reversed by the activity of serine/threonine protein phosphatases (PP1/PP2A inhibitable by okadaic acid). Via guanylyl cyclase-B (GC-B) receptor, the C-type natriuretic protein (CNP) can raise 3′,5′ cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels in cells. This cGMP can inhibit phosphodiesterase (PDE) 3 (III). If PDE 3 is inhibited, the cAMP-levels increase because degradation of cAMP is protracted. 5-HT4-receptors are also found on mitochondria, where they impair calcium ion influx. Nitric oxide (NO) synthase (NOS) can be phosphorylated and activated by PKA. NOS (inhibitable by L-NAME) can generate NO, which leads to the activation of a soluble guanylyl cyclase (GC), leading to the generation of more cGMP. Moreover, 5-HT4-receptors can activate extracellular-regulated-kinase (ERK) and increase the activity of protein kinase C via the previous activation of phospholipase C (PLC). This is achieved because PLC leads to the formation of inositol-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DG). DG can activate protein kinase C.