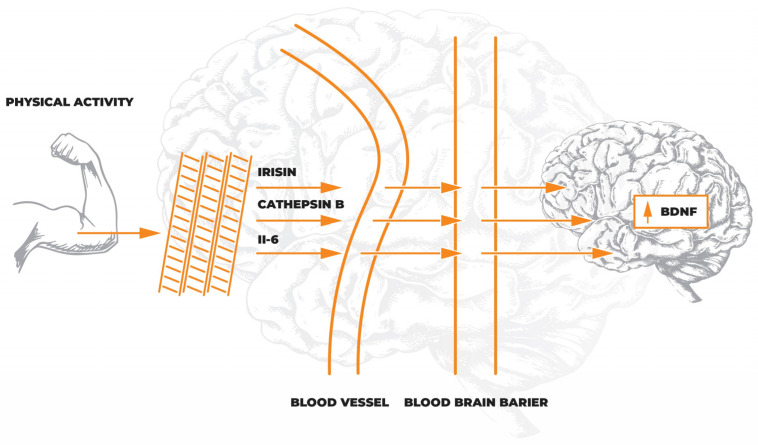
Figure 2.
Diagram of the muscle–brain endocrine loop illustrating the process of induction of plastic changes in the brain in response to physical training. Physical activity leads to the release of myokines such as interleukin-6 (Il-6), irisin, and cathepsin B into the blood by striated muscles. By penetrating the blood–brain barrier, myokines induce an increased production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), mainly in the hippocampus. The presented process leads to improved neurogenesis and induction of neuroplasticity.