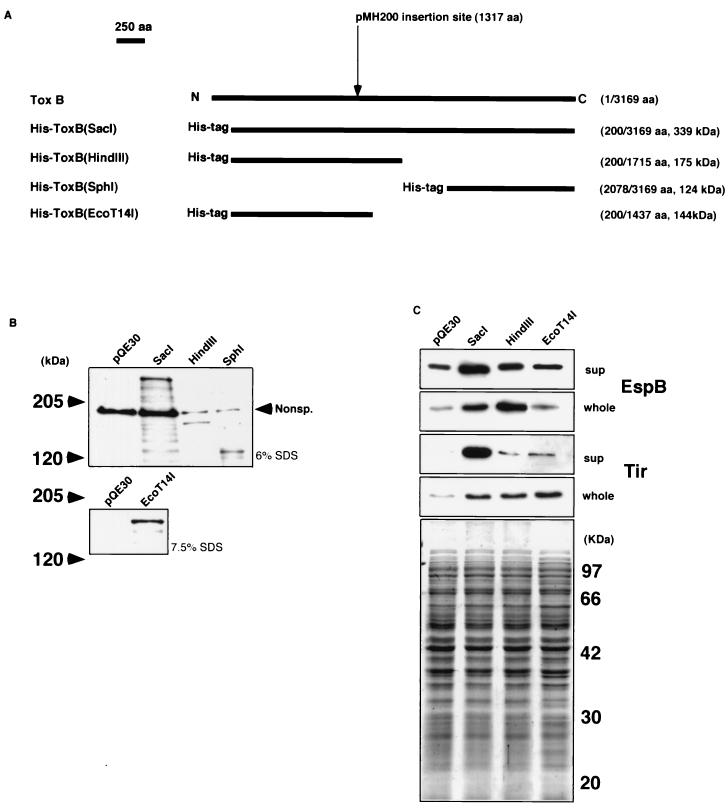
FIG. 7.
(A) Schematic maps of the truncated ToxB versions tagged with six histidines. The names of the products are indicated on the left of the maps. The numbers correspond to the positions of the amino acids (aa) in wild-type ToxB, and the predicted molecular masses are indicated on the right of the maps. The insertion site of the kanamycin resistance-encoding gene in pMH200 is indicated above the maps. (B) Expression of truncated ToxB tagged with six histidines. Trichloroacetic acid-precipitated cultures derived from equal amounts of JM109/pQE30, JM109/pHis-toxB(SacI), XL1-blue/pHis-toxB(HindIII), and XL1-blue/pHis-toxB(SphI) (upper photo) and JM109/pHis-toxB(EcoT14I) (lower photo) were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)–6% (indicated on the right of the upper photo) and –7.5% (indicated on the right of the lower photo) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with anti-RGSHHHH mouse immunoglobulin G antibody. Nonsp., a band cross-reacting nonspecifically with the serum. (C) Levels of secretion and expression of EspB and Tir by O157Cu cells with pHis-toxB(SacI), pHis-toxB(HindIII), and pHis-toxB(EcoT14I). Trichloroacetic acid-precipitated culture supernatants (sup) and bacterial cell lysates (whole) derived from the same amount of O157Cu with either pHis-toxB(SacI) derivatives or pQE30 (used as a control) were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate–12% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (bottom photo) or transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with polyclonal rabbit antiserum specific to each protein indicated at the right.