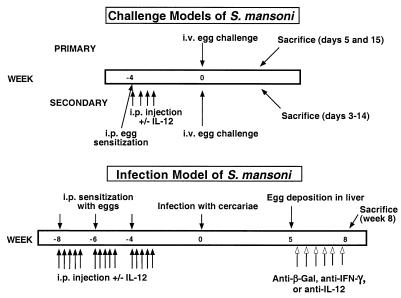
FIG. 1.
Schematic of models of S. mansoni used in this study. In the primary-challenge model, C57BL/6 mice were sacrificed at days 5 and 15 after i.v. injection of 5,000 eggs. In the secondary-challenge model, mice were sensitized i.p. with 5,000 eggs. Mice cosensitized with rIL-12 received four daily injections i.p.(0.25 μg/dose) during egg sensitization. Four weeks later, mice received 5,000 eggs i.v. without exogenous cytokines. Mice were sacrificed at days 0, 3, 6, 10, and 14 after i.v. challenge. In the infection studies, mice were sensitized with 5,000 eggs i.p. three times, with 2 weeks between sensitizations, and treated with or without rIL-12 (0.25 μg/dose) on days 0, 1, 2, 3, and 5 after each egg exposure. Four weeks after administration of the last dose of rIL-12, mice were infected with cercariae by percutaneous challenge of the tail skin. Five weeks after infection (coinciding with egg deposition), mice received neutralizing antibodies against IFN-γ, IL-12, or, as a control, β-Gal at 1 mg/dose i.p. twice weekly until they were sacrificed 8 weeks after infection.