FIG. 6.
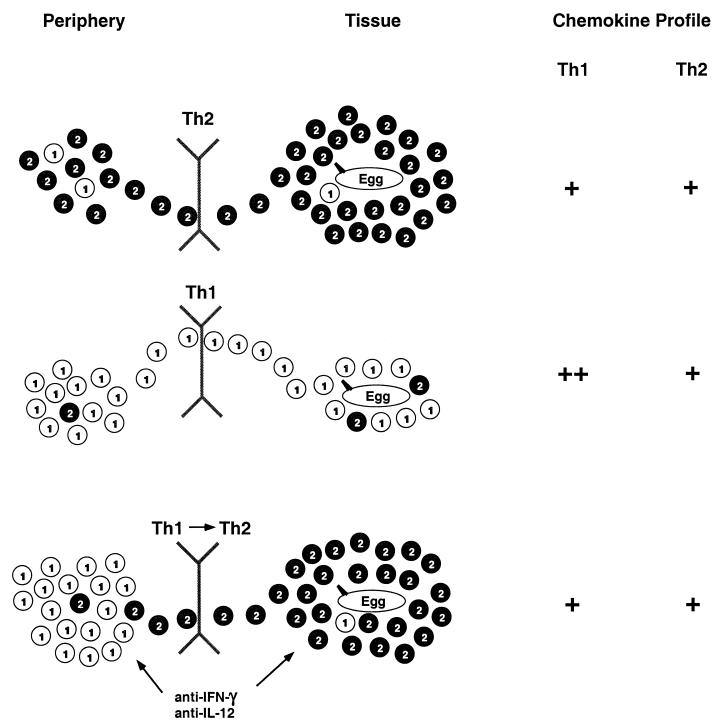
Inflammatory response to eggs in the livers of S. mansoni-infected mice depends on both the peripheral T-cell pool and the tissue pattern of chemokine expression. Th1 and Th2 cells are represented by the numbered circles. In infected mice that have not been pretreated with rIL-12 (top panel), Th2 cells predominate within the population of reactive effector-memory CD4+ T cells, and type 2 response-associated chemokines, which target these cells, are induced in the liver, together leading to the efficient recruitment of Th2 cells and characteristic hepatic granulomas and pathology. In mice sensitized along with rIL-12 (middle panel), Th1 cells predominate within the population of reactive effector-memory CD4+ T cells, and type 1 response-associated chemokines, which target these cells, are highly induced in the liver, together leading to the efficient recruitment of Th1 cells and decreased Th2 cells with diminished granulomas and pathology. In mice sensitized along with rIL-12 and treated with anti-cytokine antibodies during the time that eggs are deposited (bottom panel), although Th1 cells still predominate, some Th2 cells emerge within the population of reactive effector-memory CD4+ T cells and the cytokine blockade results in a reversal of the chemokine pattern in the liver with decreased type 1 response-associated chemokines. Together, these changes lead to the return of Th2 cells to the liver with granuloma size, composition, and pathology being restored.