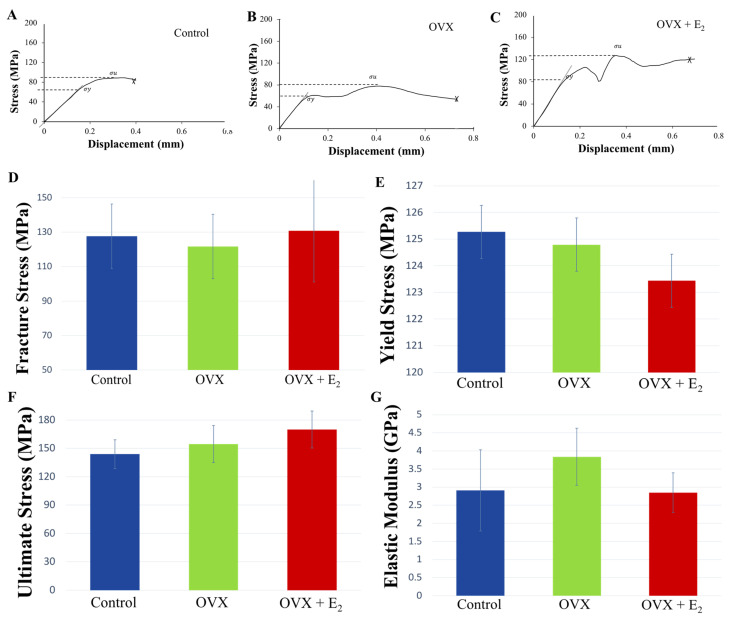
Figure 4.
Representative stress-displacement deformation plots for tibiae in the (A) control, (B) OVX, and (C) OVX + E2 groups. “Pop-in” events were present, and were attributed to either the progression of existing microcracks present within the bone structure or the initiation of new microcracks, which ultimately culminated in whole bone fracture. The mechanical properties of (D) fracture strength , (E) yield stress , (F) ultimate stress , and (G) elastic modulus E, at the tibial mid-point in the control, OVX, and OVX +E2 groups (n = 6). Means ± SE are presented in Supplementary Table S3.