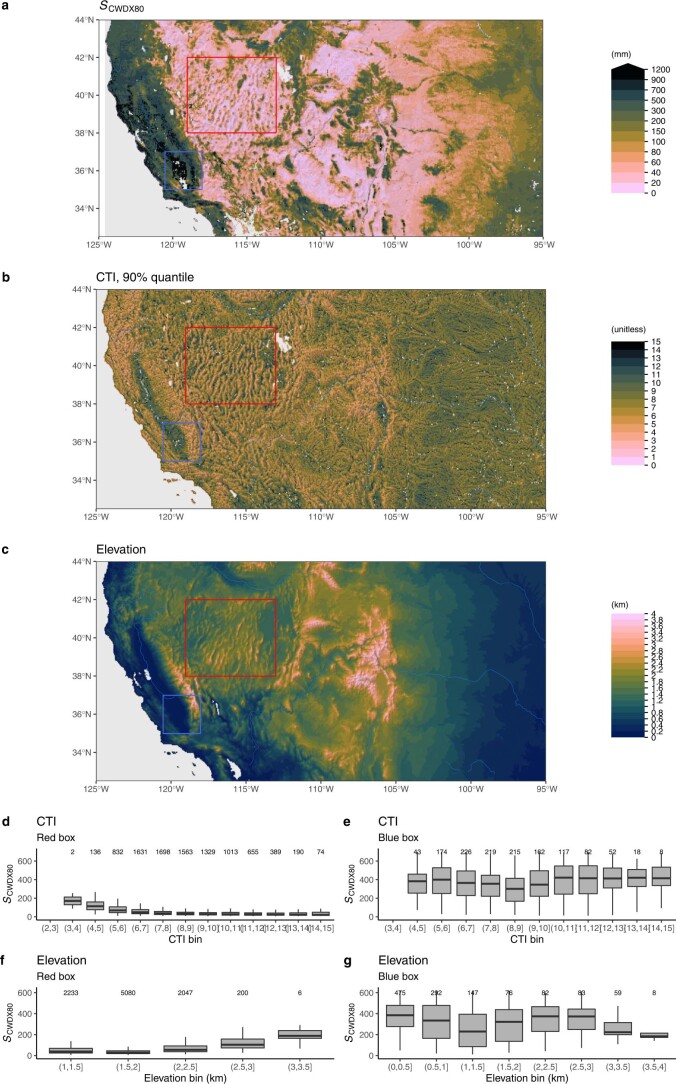
Extended Data Fig. 8. Rooting zone water storage capacity along topographic gradients in the western United States.
(a) Rooting zone water storage capacity in the western United States, estimated by the magnitude of cumulative water deficit extreme events with a return period of 80 years SCWDX80). (b) Compound Topography Index60, shown as 90% quantiles of underlying pixels, given at 15 arcsec, within matching 0.05∘ gridcells. (c) Elevation from ETOPO143. Red and blue rectangles indicate the domains for which SCWDX80 distributions along a CTI and an elevation gradient are shown in (d), (e), (f), and (g). The Compound Topography Index (CTI) is a measure for subsurface flow convergence and the water table depth based on the topographical setting61. Boxes represent the interquartile ranges of binned values (Q25, Q75), and whiskers cover Q25 − 1.5(Q75 − Q25) to Q75 + 1.5(Q75 − Q25). Numbers of data points per bin are given above boxes.