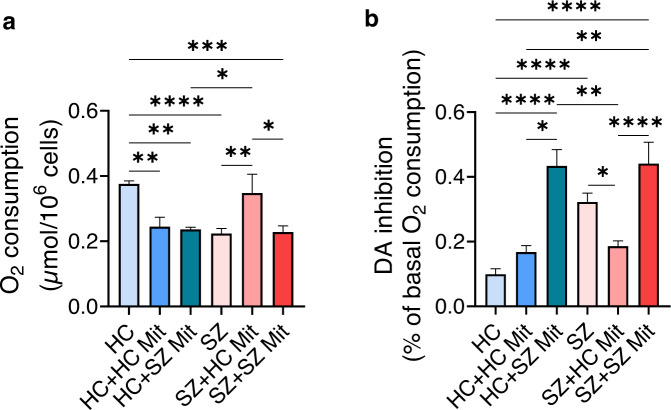
Fig. 5. Mitochondria transplantation into hLCLs affects their basal cellular respiration and its inhibition by DA, depending on disease/health conditions.
Isolated active mitochondria derived from either healthy controls (HC) or SZ patients were transplanted into HC- and SZ-hLCLs and their O2 consumption, as well as its inhibition by DA, were measured by Clark oxygen electrode five days after delivery. a Significant differences in basal O2 consumption between the six experimental groups (F(5,34) = 7.67, P < 0.0001). Reduced respiration of SZ-hLCLs (SZ vs. HC, P < 0.0003) was restored to normal levels after transplantation with mitochondria derived from HC (SZ vs. SZ + HC-Mit, P < 0.0085; HC vs. SZ + HC-Mit, P > 0.05) but remained impaired after transplantation with mitochondria isolated from SZ-hLCLs (SZ vs. SZ + SZ-Mit, P > 0.05; HC vs. SZ + SZ-Mit, P < 0.0012;). Mitochondria transplantation into HC-hLCLs impaired basal respiration regardless of mitochondria origin (HC vs. HC + HC-Mit, P < 0.0071; HC vs. HC + SZ-Mit, P < 0.0025). b One-way ANOVA shows significant differences in DA inhibition of O2 consumption between groups (F(5,36) = 15.9, P < 0.0001). Inhibition of O2 consumption by DA was increased in SZ-hLCLs as compared to HC-hLCLs (HC vs. SZ, P < 0.0001) and was attenuated to normal levels by transplanted HC-mitochondria (SZ vs. SZ + HC-Mit, P < 0.049; SZ + HC-Mit, vs. HC P > 0.05) but not by SZ-mitochondria (HC vs. SZ + SZ-Mit, P < 0.0001; SZ vs. SZ + SZ-Mit, P > 0.05). SZ-mitochondria severely increased DA inhibition in HC-hLCLs (HC vs. HC+SZ-Mit, P < 0.0001), while HC-mitochondria had no effect on DA induced inhibition of O2 consumption (HC vs. HC + HC-Mit, P > 0.05). N = 4–11 cell lines/group, measured in triplicates. All values are means ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0005.