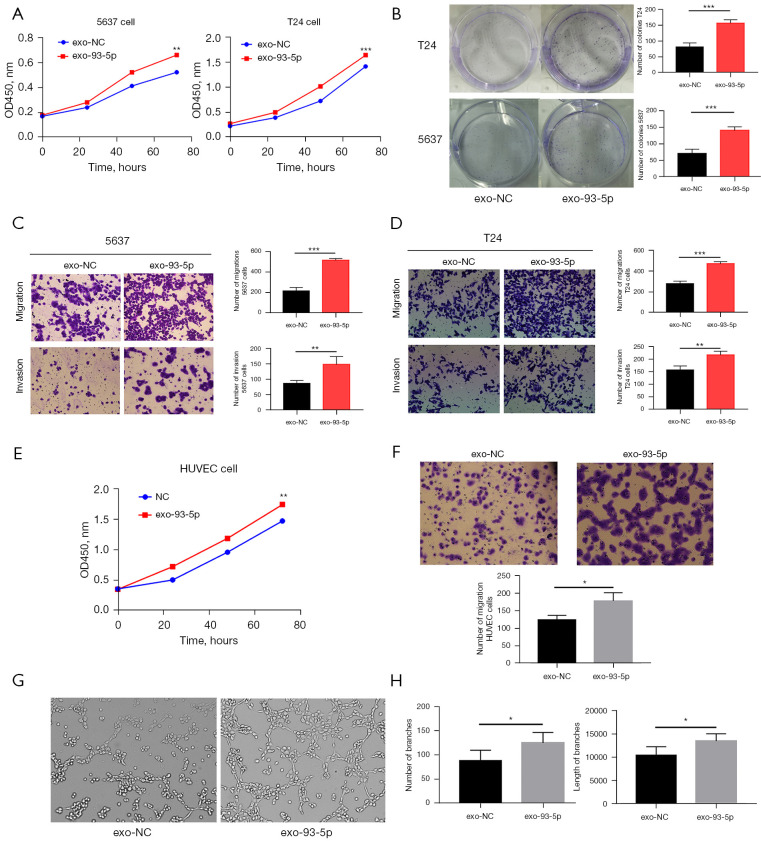
Figure 3.
The role of BLCA exosomes in cancer cells and angiogenesis. T24 cells, 5637 cells, and HUVECs were incubated with the exosomes above (Figure 2E), exosomes transfected with miR-93-5p (exo-93-5p) and exosomes transfected with negative control (exo-NC), and the migration, invasion, and proliferation of the HUVECs were assessed at 24 h. (A) T24 cells with exosomal miR-93-5p promoted the proliferation of BLCA cells. (B) The proliferation rate of T24 and 5637 cells measured by colony-forming assays. (C) Exosomal miR-93-5p promoted the cell migration and invasion in 5637 cells (magnification: 100×). (D) Exosomal miR-93-5p promoted the cell migration and invasion of T24 cells (magnification: 100×). (E) T24 cells with exosomal miR-93-5p promoted the proliferation of HUVECs. (F) Transwell assay detected the migration of exosomal miR-93-5p in HUVECs (magnification: 100×). (G) Exosomal miR-93-5p derived from T24 cells promoted the angiogenesis of HUVECs in vitro (magnification: 100×). (H) Quantitative analysis of angiogenesis data by ImageJ software. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, and ***, P<0.001. 0.1% crystal violet solution was used for cell staining in B-D and F. BLCA, bladder cancer; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells.