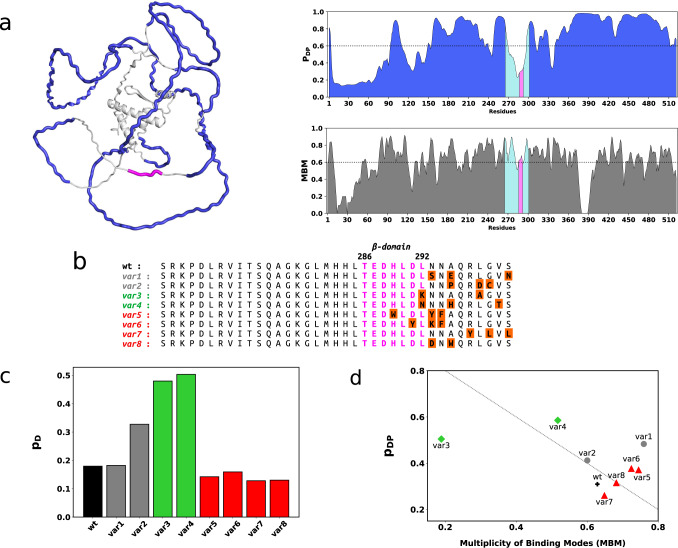
Fig. 1. Predicted structure and dynamics characteristics of the wild-type Mef2D and variant sequences.
a Mef2D is extensively disordered and predicted to form liquid-liquid phase separated condensates. The Mef2D structure predicted by Alphafold57 indicates a small structured domain involving the N-terminal ~100 residues and most of the transactivation domain (TAD) contains is disordered. The regions promoting formation of liquid-like droplets by the FuzDrop method58 are marked by blue. The β-domain (magenta) appears as an ordered motif within the disordered transactivation region. FuzDrop predictions26 shown on the right panels indicate high droplet-promoting probability (pDP) in particular for regions 155-268 residues and 341-520 residues, which are predicted to spontaneously form liquid-liquid phase separated condensates. The β-domain (magenta) and its flanking regions (cyan) are predicted to serve as ordered interaction motifs within the condensate (see also Supplementary Fig. 1). In addition, the β-domain region is capable of sampling a multiplicity of binding modes (MBM), indicating its sensitivity to the cellular context. b Sequences of the designed Mef2D variants. The β-domain and its flanking regions are shown for the wild-type (wt) Mef2D (UniProt code: Q14814; https://legacy.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q14814; 265-301 residues), var1 and var2 with similar β-domain dynamics (gray), var3 and var4 with mobile β-domains (green), var5-var8 with rigid β-domains (red) as compared to wild-type Mef2D. The sequence of the β-domain is magenta, mutated residues (orange) are highlighted. c Predicted β-domain disorder of Mef2D variants. Structural disorder in the unbound state of Mef2D were computed for the full protein sequence using the Espritz method30 as embedded in the FuzPred program25 and the pD values were averaged for residues 286-292. The var3 and var4 variants (green) are above the threshold between disorder and order (pD ≥ 0.308530). var1 (gray) has similar, var2 (gray) has slightly more mobile β-domain than the wild-type Mef2D (black). var5-var8 variants (red) are predicted to have more rigid β-domain than the wild-type. d Droplet landscape of the Mef2D variants. The droplet landscape shows the droplet probability (pDP) as a function of the multiplicity of binding modes (MBM)31,35. The assemblies below the diagonal are likely more solid-like, those above the diagonal are more liquid like33. High MBM values indicate an increased likelihood to change between liquid-like and solid-like forms, for example in case of var8. More mobile β-domain variants (var3, var4, green diamonds) exhibit increased probability to form droplets (higher pDP), whereas more rigid β-domain variants (var5-var8, red triangles) more likely form solid-like states depending on the cellular conditions (high MBM).