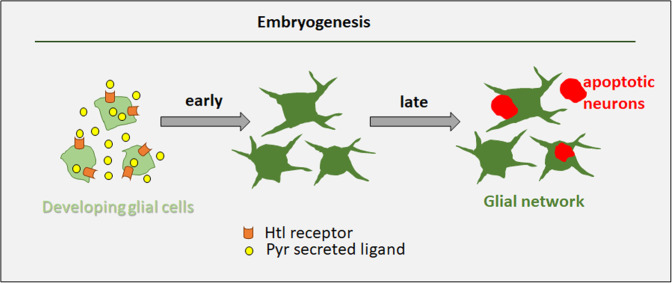
Fig. 7. Schematic representation of Htl-regulated formation of the glial network during early embryogenesis.
When glial differentiation begins, the Htl receptor is expressed in glial cells. The Htl receptor ligand Pyr is secreted from glial cells and binds Htl on glial membranes, resulting in signaling which is necessary to instruct the cytoskeleton of glial cells to grow and develop extensions. These branched glial cells form an elaborate network that is essential for clearance of apoptotic neurons later in development, when massive neuronal apoptosis takes place in the embryonic CNS. Reduction in Pyr or Htl levels disrupts the glial network and impairs the removal of dying neurons. Accumulation of uncleared dying cells may lead to developmental defects, inflammation and neurodegeneration later on.