Figure 2.
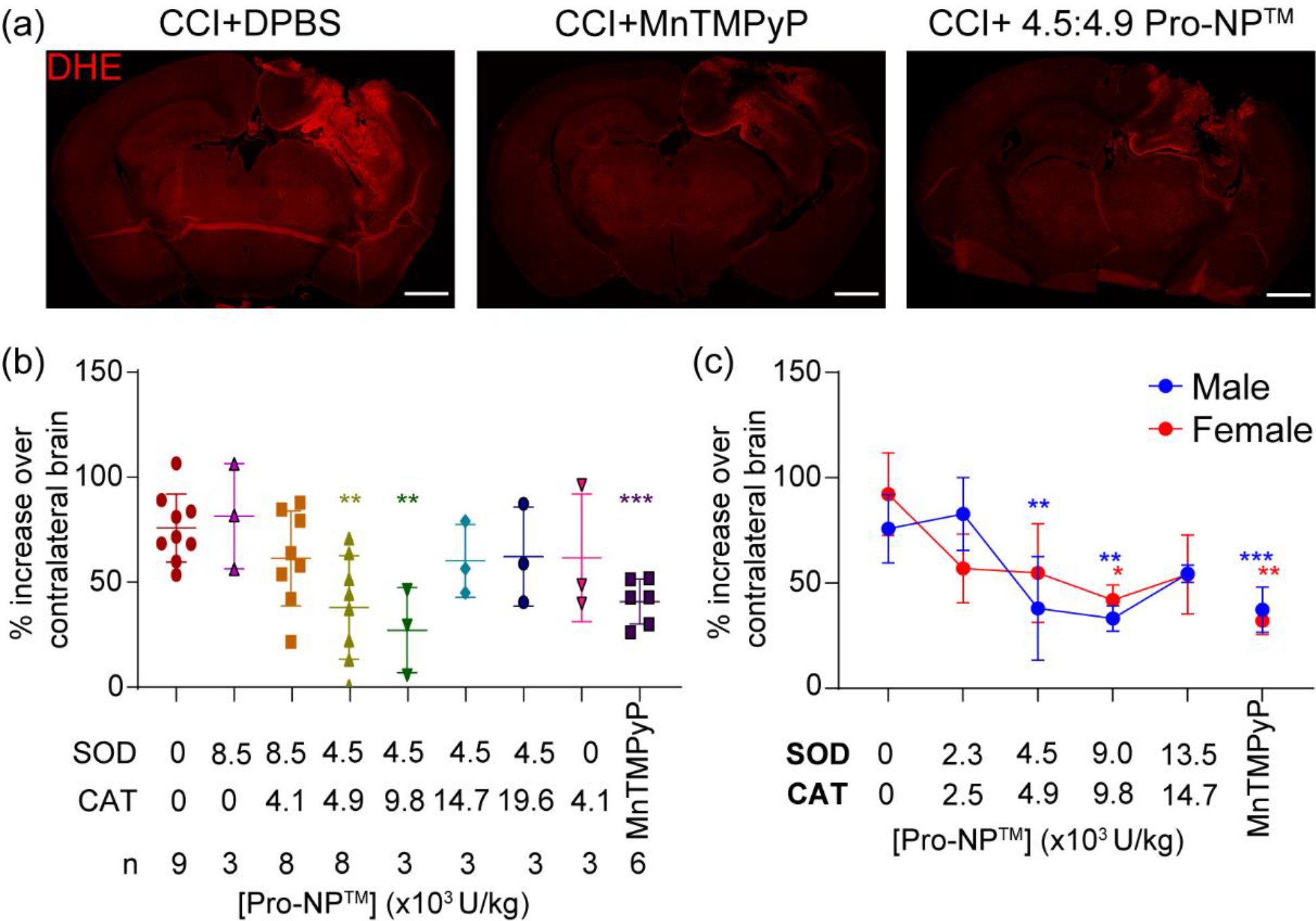
Identifying the optimum SOD1:CAT activities of Pro-NP™. In vivo DHE staining of the brains at 4 h post-injury was utilized to measure the ROS level in the acute phase of injury. Various concentrations and ratios of SOD1:CAT-Pro-NP™ were administered to find the optimum concentration in reducing ROS. (a) Representative confocal microscopy images of control, MnTMPyP, and 4.5:4.9 SOD1:CAT-Pro-NP™ following CCI in male mice. Scale bar is 1 mm. (b&c) Quantification of DHE fluorescence mean intensity at the perilesional normalized to the contralateral hemisphere with various SOD1:CAT-Pro-NP™ ratios in male CCI mice (b), and various concentrations of 1:1 SOD1:CAT-Pro-NP™ in male and female CCI mice (c). Data are shown as mean ± SD with n = 3 for female mice, and n = 3–9 for male mice. * indicates a statistical difference compared to the 0 mg/kg Pro-NP™ group, with one, two, and three symbols indicating p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively, as determined by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc test.
