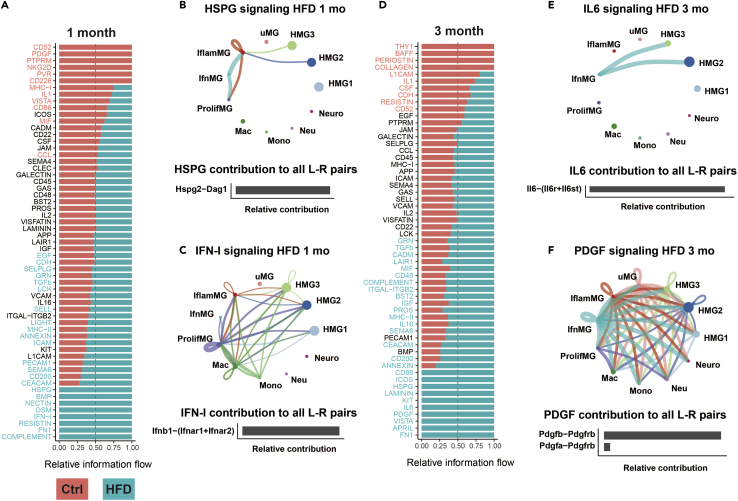
Figure 5.
Cell-to-cell communication analyses reveal HFD specific intercellular communication pathways
(A) Information flow charts at 1 month for HFD (blue) versus control (ctrl; red) generated by CellChat. Teal bars represent information flow in HFD cells (4,555 total cells), red bars represent information flow in control cells (4,945 total cells). Signaling pathways in teal text have significantly higher information flow in HFD cells relative to control, signaling pathways in red text have significantly higher information flow in control cells, and signaling pathways in black text are not significantly different between groups; vertical dashed lines represent information flow equal in both HFD and control.
(B and C) Circle plots of cellular signaling interactions (top) and their top contributing ligand-receptor (L-R) pairs (bottom) for pathway networks involving (B) HSPG for HFD at 1 month and (C) IFN-I for HFD at 1 month. Dots in circle plots represent cell populations with color codes matching UMAP clusters; strokes represent communication between distinct cell populations and loops represent signaling within cell populations. Stroke and loop colors reflect the cluster sending the signal, and thickness reflects strength of the signaling pair.
(D) Information flow chart at 3 months for HFD (blue; 1,292 total cells) versus control (ctrl; red; 1,255 total cells).
(E and F) Circle plots (top) and top contributing L-R pairs (bottom) for pathway networks involving (E) IL6 for HFD at 3 months and (F) PDGF for HFD at 3 months.