FIGURE 3.
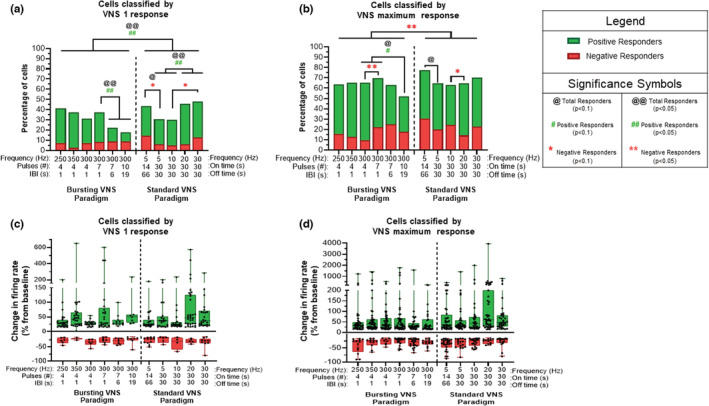
Magnitude firing rate changes across VNS paradigms in the LC. (a) The percentage of responder cells for each stimulation paradigm compared to their baseline level for VNS 1 is shown, with negative responders (>15% decrease), non‐responders (−15— + 15% change) and positive responders (>15% increase). For VNS 1, standard paradigms yield more positive and total responders than bursting paradigms (p < 0.05). For bursting paradigms at 300 Hz, increasing IBI to 6 s or 19 s or the pulse number from 7 to 10 decreased the number of total and positive responders (p < 0.05). While shorter on times during standard VNS drive more negative and total responders at 5 Hz (14 s vs. 30 s) (p < 0.1), higher standard frequencies (20/30 Hz) yield more positive and total responders than lower standard frequencies (5/10 Hz, p < 0.05). Additionally, negative responders are increased at 30 Hz compared to 10 Hz (p < 0.1). (b) The percentage of responder cells in each VNS paradigm were also classified according to their maximum response over the 5 VNS cycles. Note that no correlation was found of VNS response to any particular stimulation cycle. Overall, the standard paradigms have greater negative responders compared to bursting paradigms (p < 0.05). For standard paradigms, an “on time” of 30 s versus 14 s (5 Hz) showed fewer total responders (p < 0.1). Standard 20 Hz VNS yields decreased negative responders compared to 10 Hz (p < 0.1). For bursting paradigms at 300 Hz, increasing IBI to 19 s along with the pulse number from 4–7 to 10 decreased the number of total and positive responders (p < 0.1) and negative responders are increased with seven pulses compared to four pulses (p < 0.05). The boxplot graphs on the bottom row display 2.5, 25, 50, 75, and 97.5 percentiles of the relative strength for neuronal responses from their baseline activity during VNS 1 (c) and VNS Max (d). Although positive responders displayed a significant difference across all 11 paradigms, there were no significant post hoc results. No significant differences existed between paradigms for negative responders. @ p < 0.1, # p < 0.1, *p < 0.1, @@ p < 0.05, ## p < 0.05, **p < 0.05.
