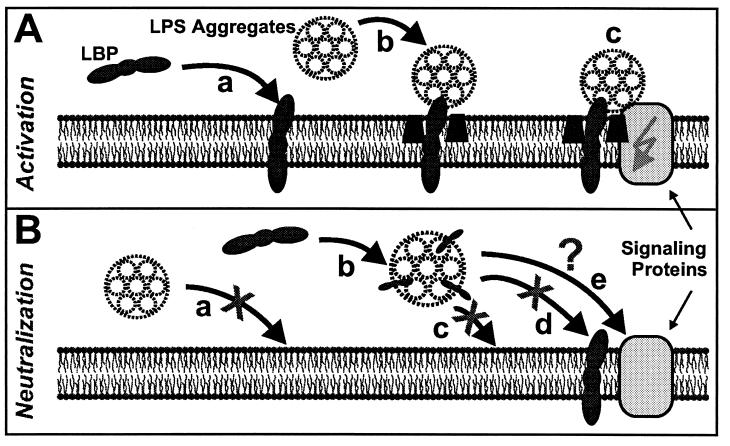
FIG. 7.
Cartoon of proposed mechanisms of interaction between LBP, LPS, and phospholipid membranes independent of membrane-bound CD14. (A) Interactions that may be involved in the LPS-induced activation of MNC: intercalation of LBP into the membrane (a), LBP-mediated binding and/or intercalation of LPS (different scales were used for the cartoons of LPS aggregates in solution and in membrane-intercalated LPS) (b), and activation of MNC by signaling proteins such as Toll-like receptors or ion channels (c). (B) Interactions that may cause neutralization of LPS by LBP: LPS aggregates do not bind to or intercalate into lipid membranes (a), LBP intercalates into LPS aggregates (b), and LPS/LBP complexes do not bind to or intercalate into lipid membranes (c) or bind to LBP-doped membranes (d), whereas binding to other components of MNC is still possible (e).