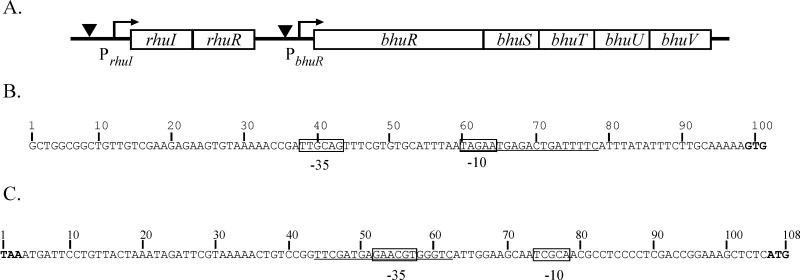
FIG. 2.
Genetic organization of the rhuIR-bhuRSTUV locus of B. avium. (A) Schematic of the organization of the rhu-bhu locus in B. avium. rhuI and rhuR are homologous to genes encoding ECF sigma factor regulatory systems. bhuR has been shown to encode an outer membrane heme receptor (Murphy and Connell, unpublished). bhuSTUV are homologous to accessory genes of other known heme and hemoglobin receptors. Arrows denote putative promoter sequences. Inverted triangles represent putative Fur binding sites. The map is not drawn to scale. (B) Nucleotide sequence 5′ of the rhuI ORF contains sequences homologous to ς70-type promoters. The putative −35 and −10 regions of the PrhuI promoter are boxed. Underlined sequences share 13 of 19 nucleotides with the consensus E. coli Fur operator sequence (7). The GTG start codon of rhuI is indicated in bold type. (C) Nucleotide sequence of the 102-bp rhuR-bhuR intergenic region contains sequences homologous to ECF-dependent promoters. Nucleotides are numbered from the TAA stop codon of rhuR (bold) to the ATG start codon of bhuR (bold). Putative −35 and −10 regions of the RhuI-dependent bhuR promoter are boxed. Nucleotide sequences which have identity at 8 of 19 nucleotide positions with the E. coli consensus Fur operator sequence (Fur box) (7) are underlined.