Fig. 2 |. Regulatory sites activated in mCRPC coincide with prostate developmental programs.
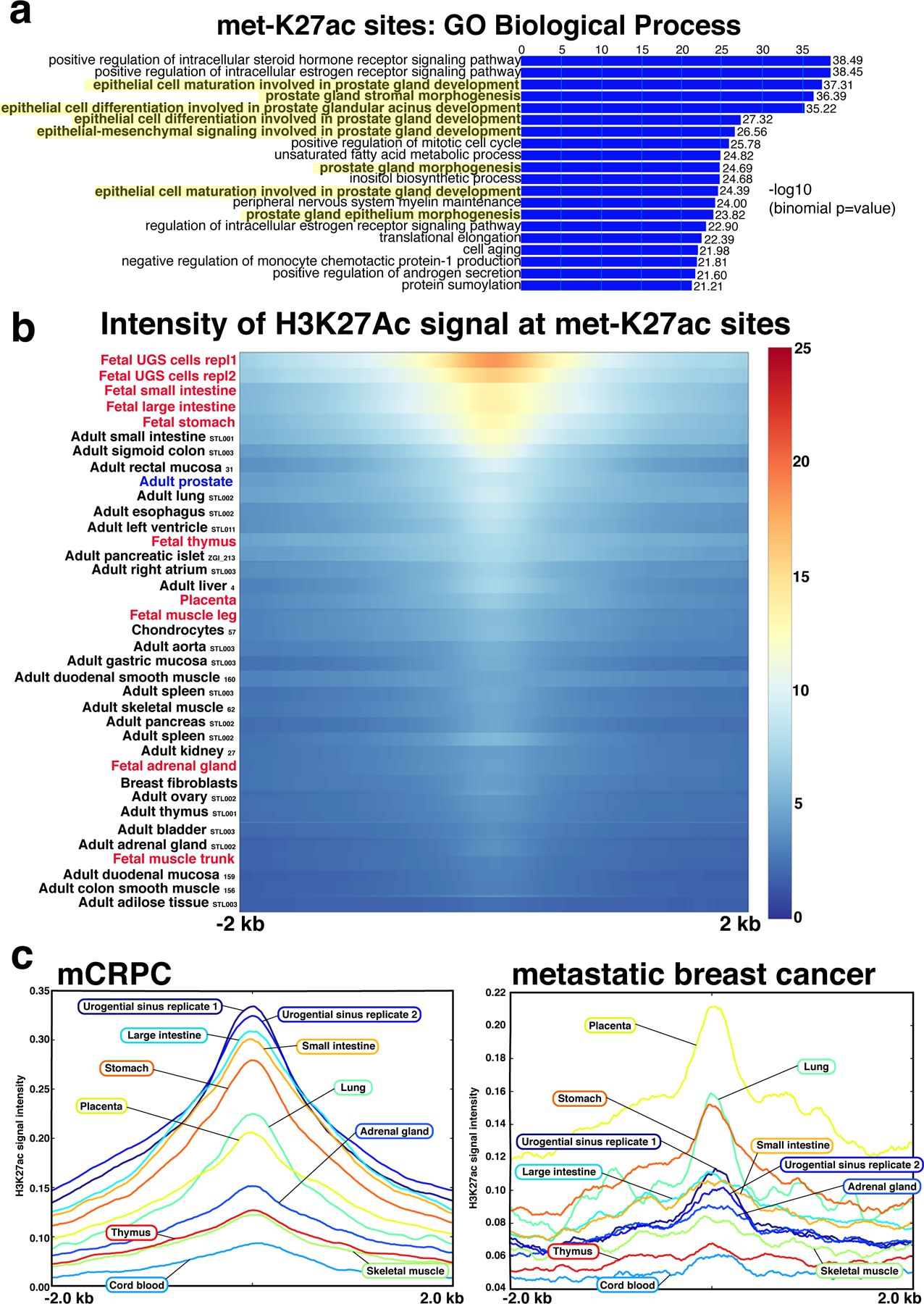
a, GREAT analysis characterizing the Gene Ontology biological terms most significantly associated with genes proximal to the 16,047 met-K27ac sites. Terms associated with genitourinary development are highlighted in yellow. b, Across 37 human adult and fetal cell types, met-K27ac is most strongly associated with fetal urogenital sinus. Cell type listed at left (adult tissues are followed by Roadmap Epigenomics Project identification codes). Urogenital sinus sample was performed in replicate. Heat map indicates H3K27ac binding intensity met-K27ac sites across a 4-kb interval. c, met-K27ac is associated with a set of fetal programs distinct from the fetal programs associated with the metastatic breast cancer-specific genome-wide H3K27ac signal. Each curve represents H3K27ac intensity in human fetal cells across the 16,047 met-K27ac sites (left) and the metastatic breast cancer-specific H3K27Ac sites (right).
