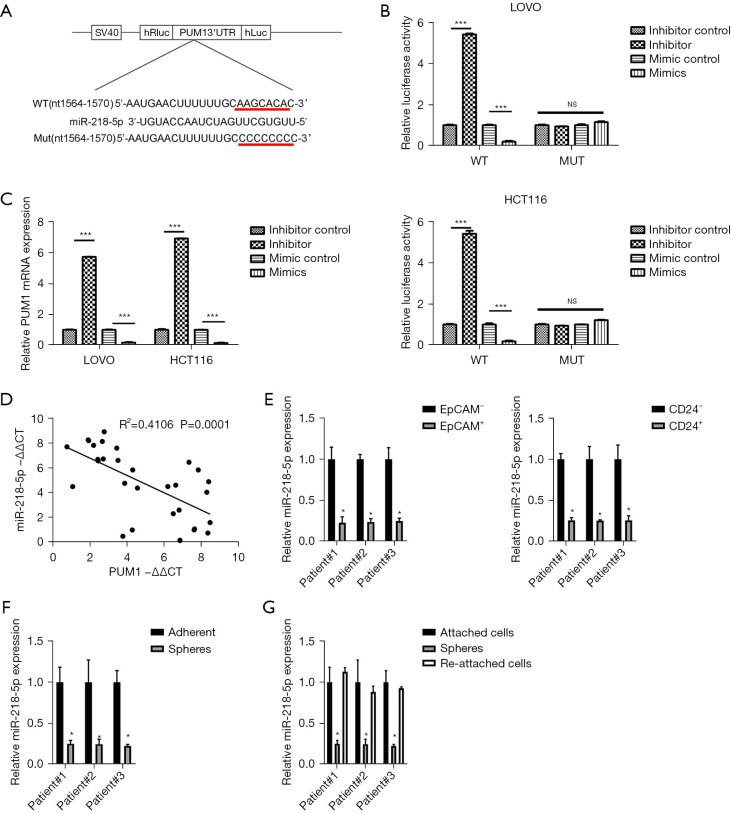
Figure 4.
miR-218-5p inhibited T-IC expansion by targeting PUM1 in CRC. (A) Potential target site predicted by TargetScan for miR-218-5p in the 3'-UTR of human PUM1 mRNA. The target site was mutated for disrupting the interaction between PUM1 mRNA and miR-218-5p. (B) Luciferase reporter assays conducted on MUT PUM1 3'-UTR or WT constructs. (C) Real-time PCR analysis of PUM1 expression in indicated CRC cells. (D) Real-time PCR analysis was used to determine the correlation between the level of PUM1 and miR-218-5p in primary CRC cells (n=30). (E) Real-time PCR analysis of miR-218-5p expression in sorted EpCAM+ or CD24+ primary CRC cells relative to negative cells. (F) Real-time PCR analysis of miR-218-5p expression in primary CRC adherent spheres and cells. (G) Real-time PCR analysis of miR-218-5p expression in primary CRC adherent, spheres, and re-adherent cells. All results are presented as the mean ± SD, and statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001; NSP>0.05. PUM1, pumilio homologous protein 1; 3'-UTR, 3'-untranslated region; WT, wild-type; MUT, mutant; mRNA, messenger RNA; CT, cycle threshold; EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; T-IC, tumor-initiating cell; CRC, colorectal cancer; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; SD, standard deviation.