Figure 4.
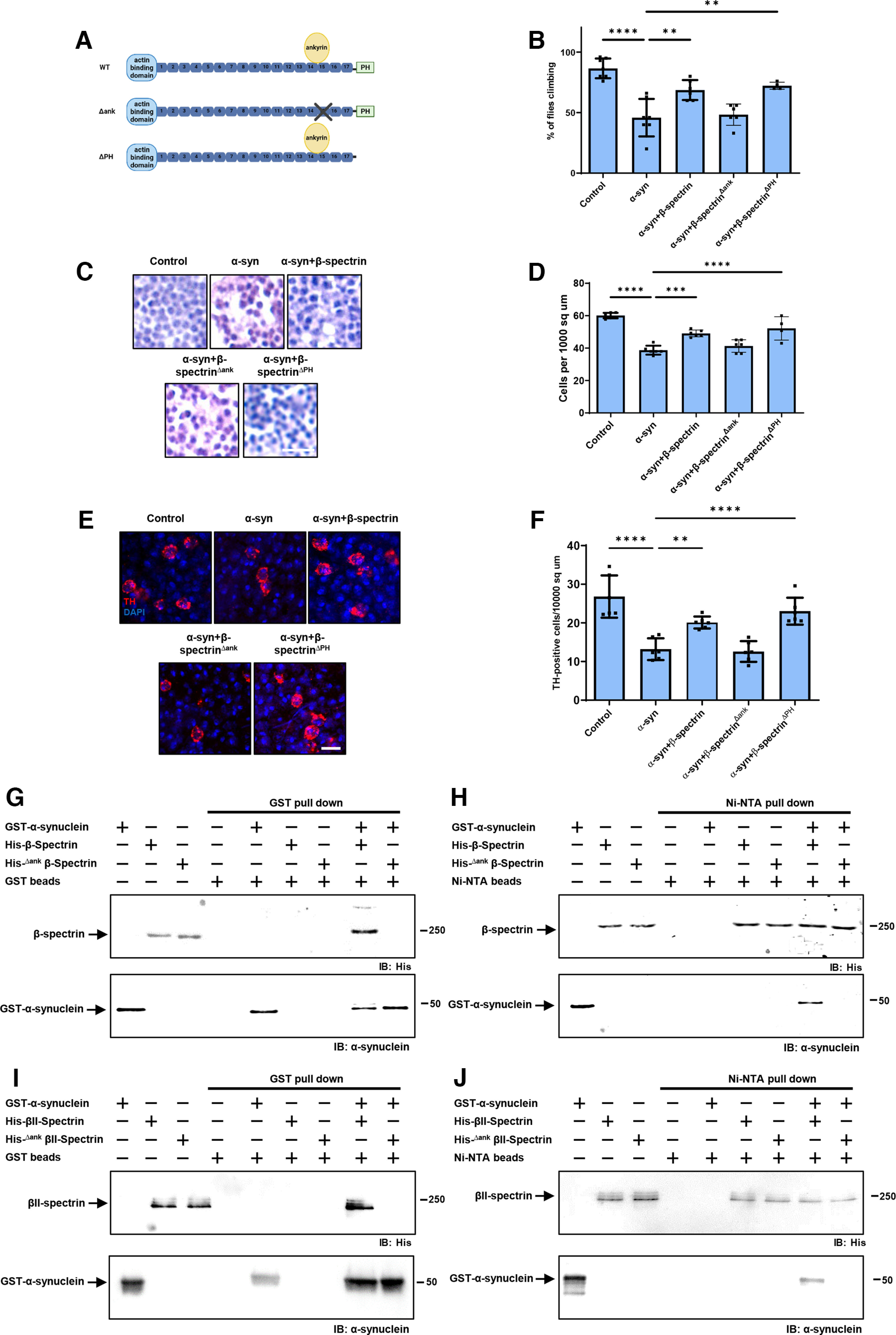
The ankyrin binding domain of β-spectrin mediates interactions with α-synuclein. A, Schematic diagram of the domains of WT β-spectrin and the two mutant versions of spectrin used (β-specΔank and β-specΔPH). B, Climbing activity in control and human α-synuclein transgenic Drosophila with and without elevated expression of WT and mutant forms of β-spectrin. n = minimum of 60 flies per genotype (six biological replicates of 10 flies each). C, D, Brain degeneration assayed by hematoxylin staining in the anterior medulla of control and α-synuclein transgenic Drosophila with and without elevated expression WT and mutant forms of β-spectrin. n = 6. E, F, Immunostaining for TH in the anterior medulla of control and α-synuclein transgenic Drosophila with and without elevated expression WT and mutant forms of β-spectrin. n = 6. G, H, Human α-synuclein and WT Drosophila β-spectrin, but not β-specΔank, interact in GST (G) or Ni-NTA (H) pull-down assays as monitored by immunoblotting for β-spectrin (His) or α-synuclein. I, J, Human α-synuclein and WT βII-spectrin, but not βII-specΔank, interact in GST (I) or Ni-NTA (J) pull-down assays as monitored by immunoblotting for β-spectrin (His) or α-synuclein. All flies are 10 d old. Control flies are nSyb-QF2, nSyb-GAL4/+. Scale bars: A, 5 µm; C, 10 µm. Data are mean ± SEM. p values determined with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test.
