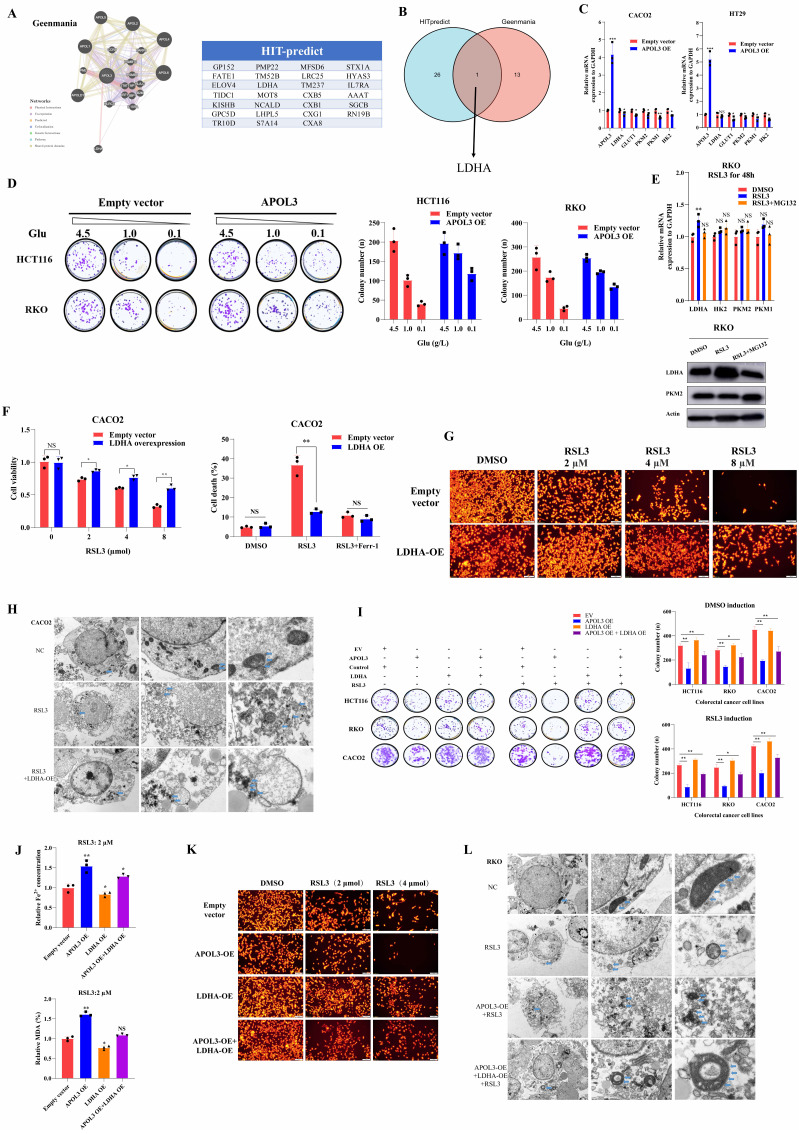
Figure 4.
APOL3-LDHA axis regulated ferroptosis in CRC. (A) PPI prediction from Gennmania and HIT-predict was performed (B) LDHA was screened as the only overlapped gene; (C) mRNA levels changes were shown after alteration of APOL3; (D) biological effect of APOL3 were highly addicted to glucose, and gradient deprivation of glucose inhibited their viability compared to negative controls; (E) treatment of RSL3 upregulated mRNA the expression of LDHA and this effect can be partly diminished with addition of MG132; (F) by CTG assay and cell death rates evaluation, overexpression of LDHA inhibits RSL3-induced ferroptosis in CACO2; (G) TMRE analysis demonstrated that overexpression of LDHA significantly inhibits ferroptosis of colon cancer cells; (H) by electron image microscopy, LDHA-OE significantly prevent cellular responses from RSL3 in CACO2 cells; (I) by clone formation analysis of CRC cell lines HCT116, RKO and CACO2, overexpression of LDHA can rescue APOL3-OE induced inhibition of cell proliferation and cell death; (J) concentration of Fe2+ and MDA (%) was also rescued after LDHA was overexpressed in CRC cells; (K) TMRE analysis found that LDHA-OE can rescue APOL3-OE-induced sensitivity to ferroptosis; (L) similar cellular response was shown by electron images. Abbreviations: CRC, colorectal cancer; PPI, protein-protein interaction; CTG, Cell Titer-Glo luminescent assay; TMRE, Tetramethylrhodamine Ethyl Ester assay.