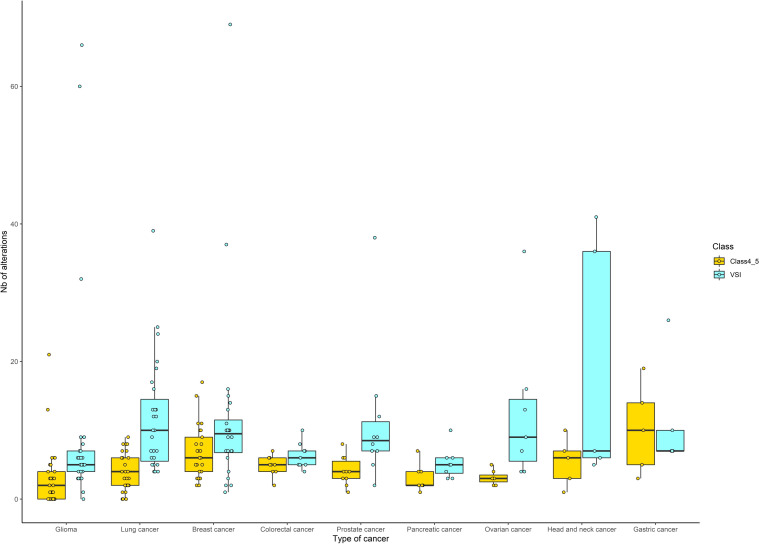
Figure 2.
Distribution of the number of genetic alterations identified by sequencing (according to cancer type). For each tumor type, genetic alterations were classified into class 4/5 (corresponding to known and/or likely pathogenic) or VUS (corresponding to variant of unknown significance). Only tumor types with at least five cases were included and are presented according to decreasing number of patients: glioma (n=36), lung cancer (n=29), breast cancer (n=25), colorectal and prostate cancers (n=10), pancreatic cancer (n=9), ovarian cancer (n=7), head and neck cancer (n=6), and gastric cancer (n=5). Boxes indicate the median and quartile values, and points correspond to the number of alterations retrieved for each patient. Yellow or blue correspond to class 4/5 or VUS, respectively.