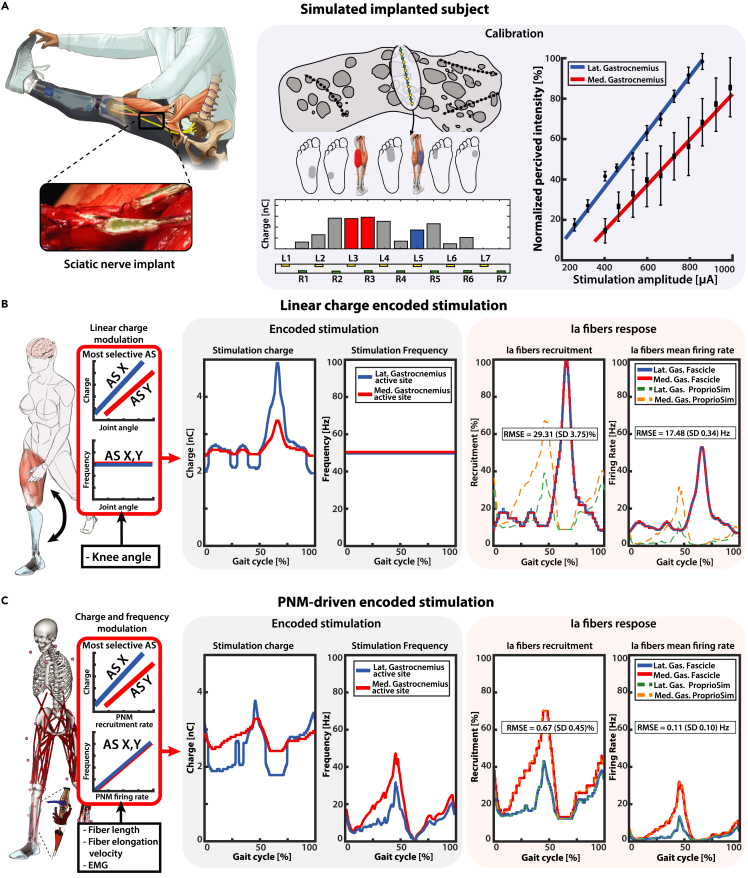
Figure 6.
PNM-driven encoding stimulation in-silico simulations
(A) A virtual subject is modeled after the previously acquired data of Subject 2. In each modeled electrode placement, stimulation of the most selective active sites for each identified potential gastrocnemius fascicle is encoded using two different types of strategies: standard linear encoding and novel PNM-driven encoding. Calibration is performed using linear interpolation between reported percived sensations and related stimulation amplitude: the obtained calibration curve is reported on the right pannel with standard deviation for repeated measures.
(B) The recorded knee angle is used to modulate linearly the stimulation impulse charge between the minimal and maximal charge levels; stimulation impulse frequency is kept constant. The resulting time-varying charge encoding parameters are presented in the central block. On the right, Ia fiber stimulation-derived recruitments and mean firing rate are displayed and compared with the PNM estimated natural activity.
(C) The PNM estimated natural Ia fibers recruitment is used to modulate linearly the stimulation impulse charge between the minimal and maximal charge levels; stimulation impulse frequency is instead obtained by dividing the estimated mean firing rate and the fibers recruitment. The resulting time-varying charge and frequency encoding parameters are presented in the central block. On the right, Ia fiber stimulation-derived recruitments and mean firing rate are displayed and compared with the PNM estimated natural activity. The presented plots and RMSE values refer to a single fascicle combination and fiber population disposition. Comprehensive results for all the simulations are displayed in Figure S2.